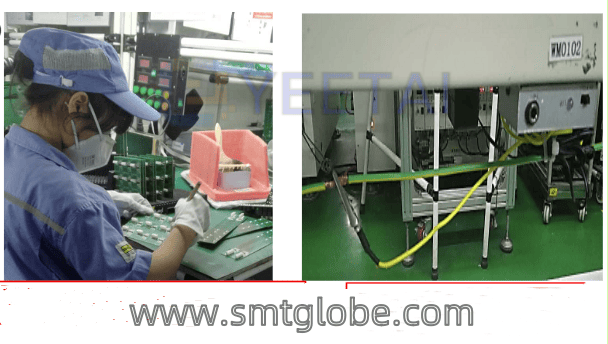
Static electricity is an unseen force that can have significant impacts on electronics. In this blog post, we’ll explore common static electricity phenomena, how it’s generated, its associated hazards, and essential anti-static measures you can implement in your workplace.
What is Static Electricity?
Static electricity occurs when there is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. Commonly generated through processes such as contact separation, friction, and induction, this phenomenon can cause problems in sensitive electronic environments.
Key Ways Static Electricity is Generated:
- Contact and Separation: When two materials come into contact and then separate, electrons can transfer from one to the other.
- Friction: Rubbing two materials together can also cause charge separation.
- Induction: The presence of an electrical charge can induce a charge in another object without direct contact.
Why Should You Be Concerned About Static Electricity?
Static electricity can pose significant risks to electronic components. Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can lead to failures, affecting the reliability and longevity of crucial devices.
Impacts of ESD Include:
- Damage to sensitive electronic components, leading to costly repairs or replacements.
- Annual losses in the electronics industry estimated at over $5 billion due to static electricity incidents, highlighting the need for preventive measures.
Recognizing the Difference: Static Electricity vs. ESD
It’s essential to differentiate between static electricity and ESD:
- Static Electricity: A stationary charge that can build up on surfaces.
- Electrostatic Discharge (ESD): The sudden flow of electricity between two objects caused by contact, an electrical short, or dielectric breakdown.
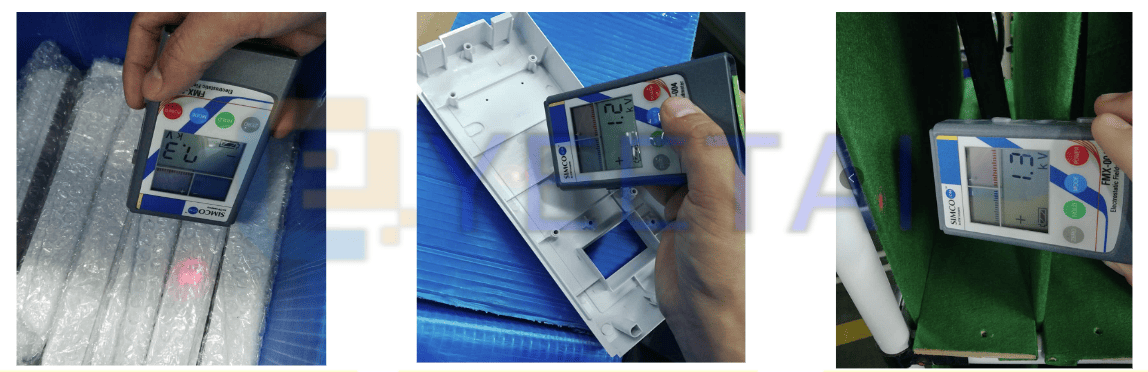
Basic Anti-Static Requirements for Electronics Workstations
To mitigate the risks associated with static electricity in electronic work environments, adhere to the following basic anti-static requirements:
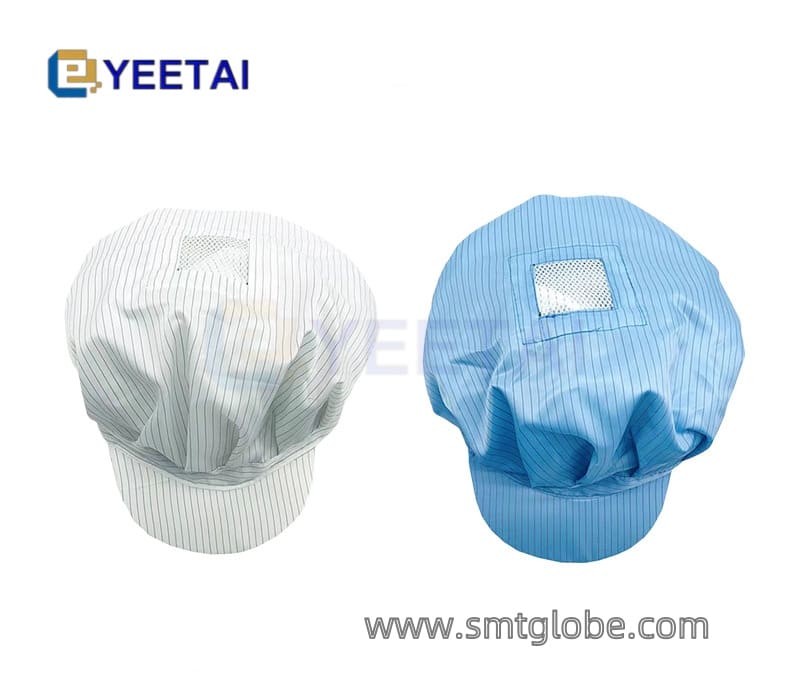
- Wear Anti-Static Clothing: Don anti-static garments and hats to reduce static buildup.
- Use Anti-Static Footwear: Invest in anti-static shoes or shoe covers.
- Conduct Body Resistance Testing: Pass through an anti-static turnstile or use a body resistance tester to ensure safe levels before entering sensitive areas.
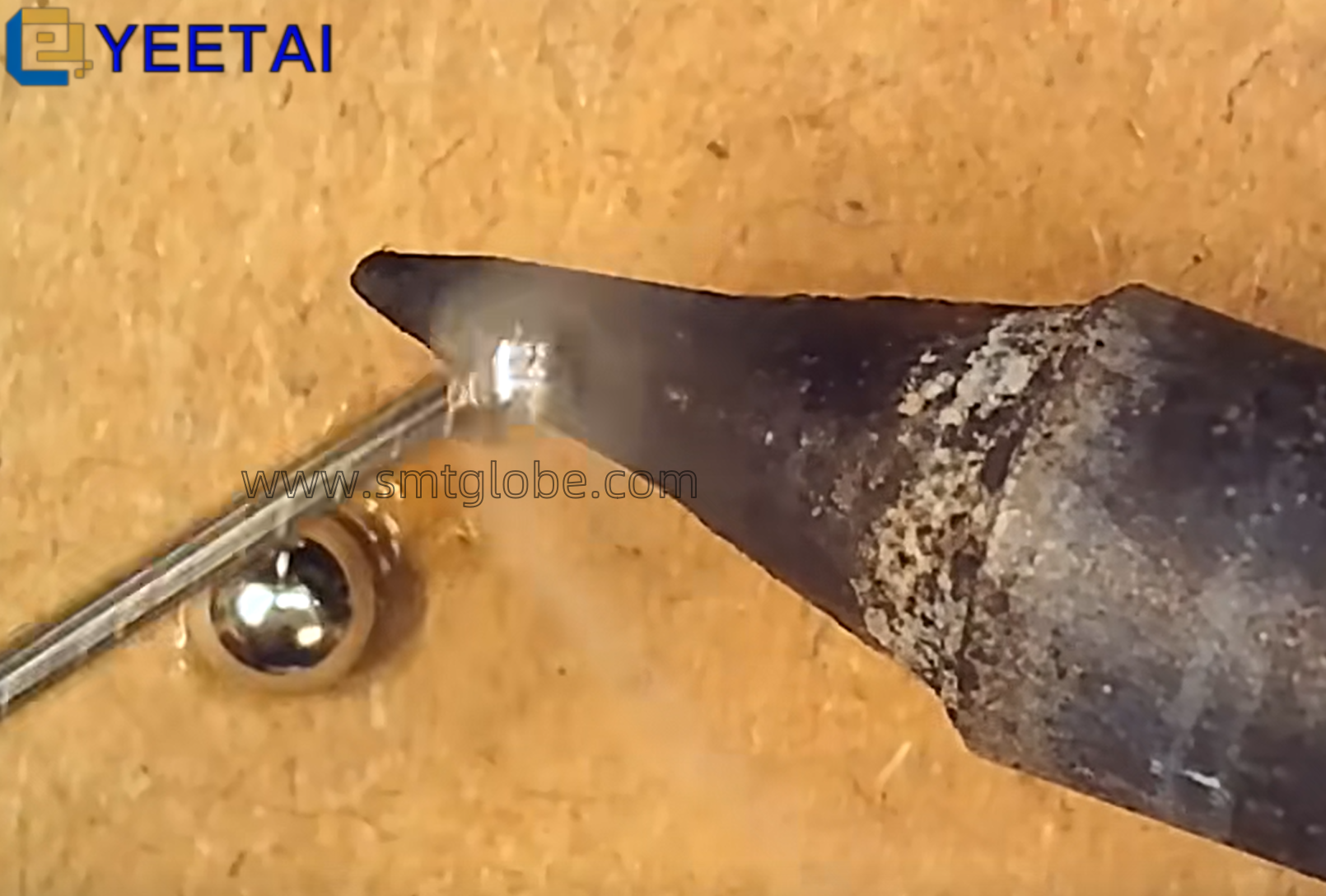
- Utilize Anti-Static Discharge Tools: Techniques like using discharge balls can effectively neutralize static charges.
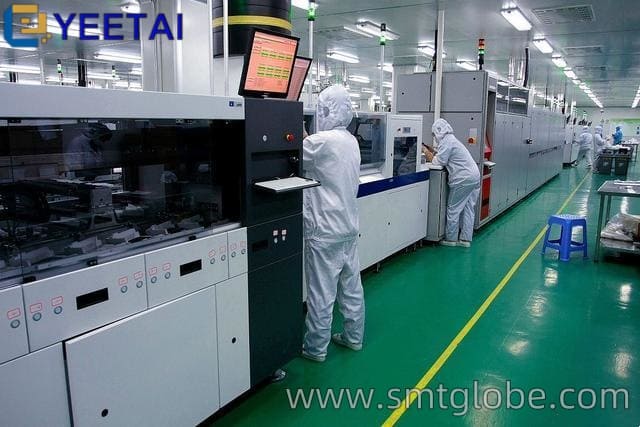
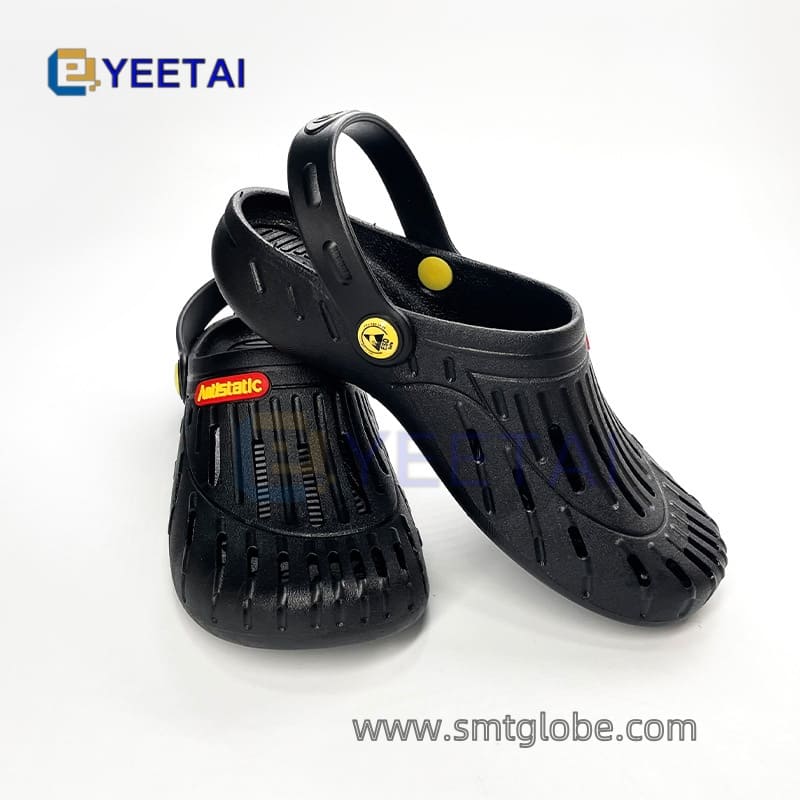



Effective Static Control Measures for Workstations
In addition to dressing appropriately, consider implementing these workstation-specific anti-static measures:
- Wear Anti-Static Wrist Straps: For operators handling sensitive components, attaching the wrist strap to a grounding system is crucial.
- Utilize Anti-Static Gloves: Gloves provide additional protection while handling electronic components.
- Install Anti-Static Flooring: Consider using anti-static mats or flooring in work areas for effective electrostatic control.
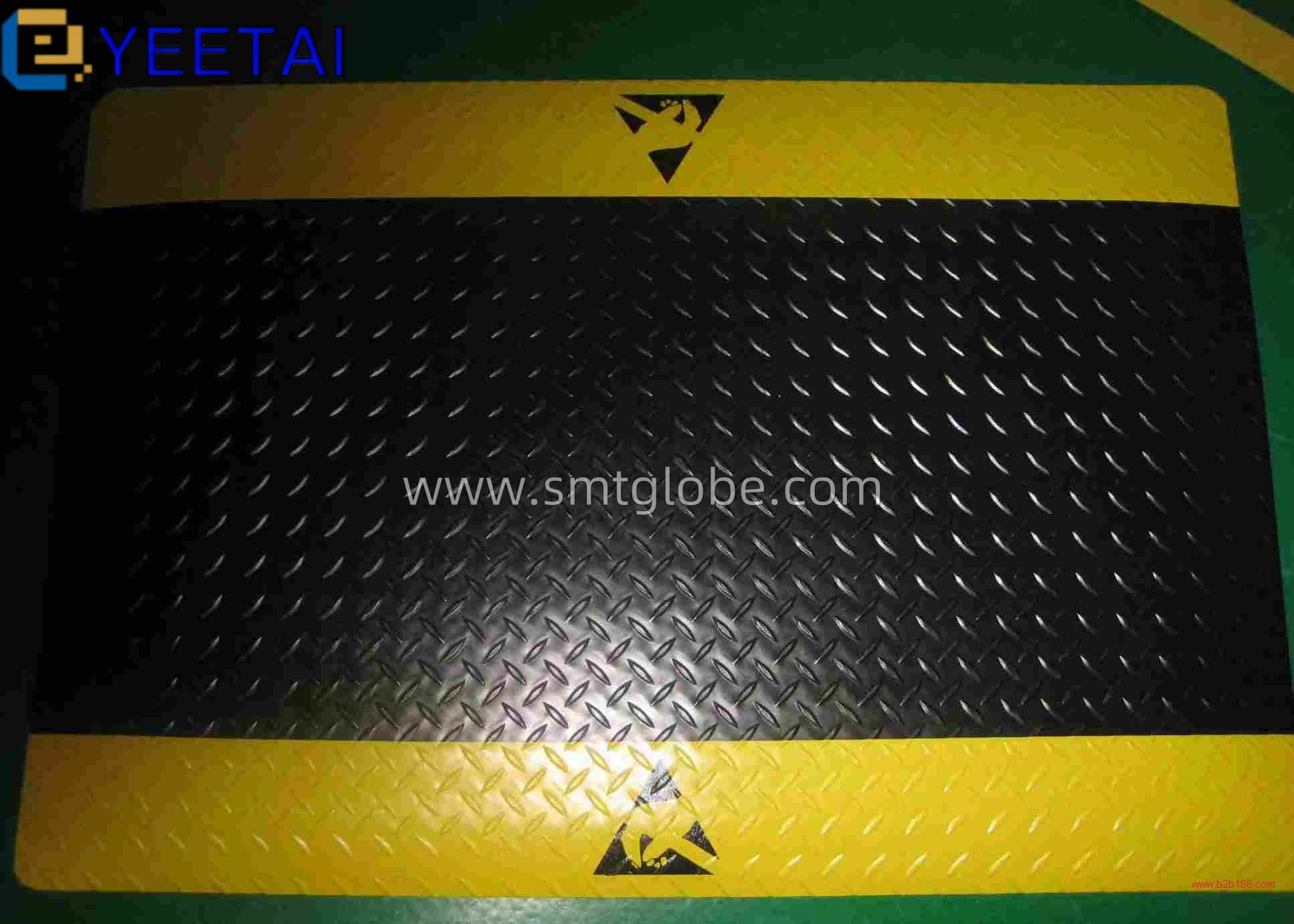
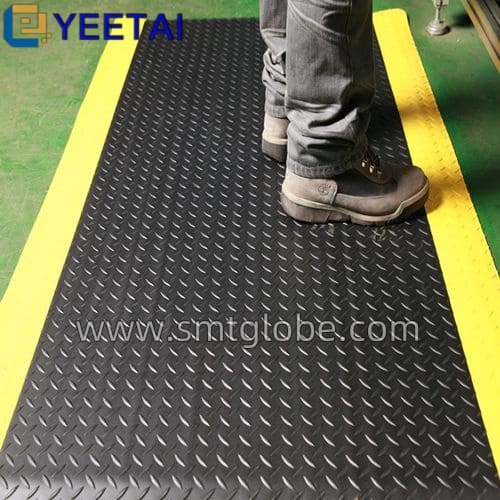
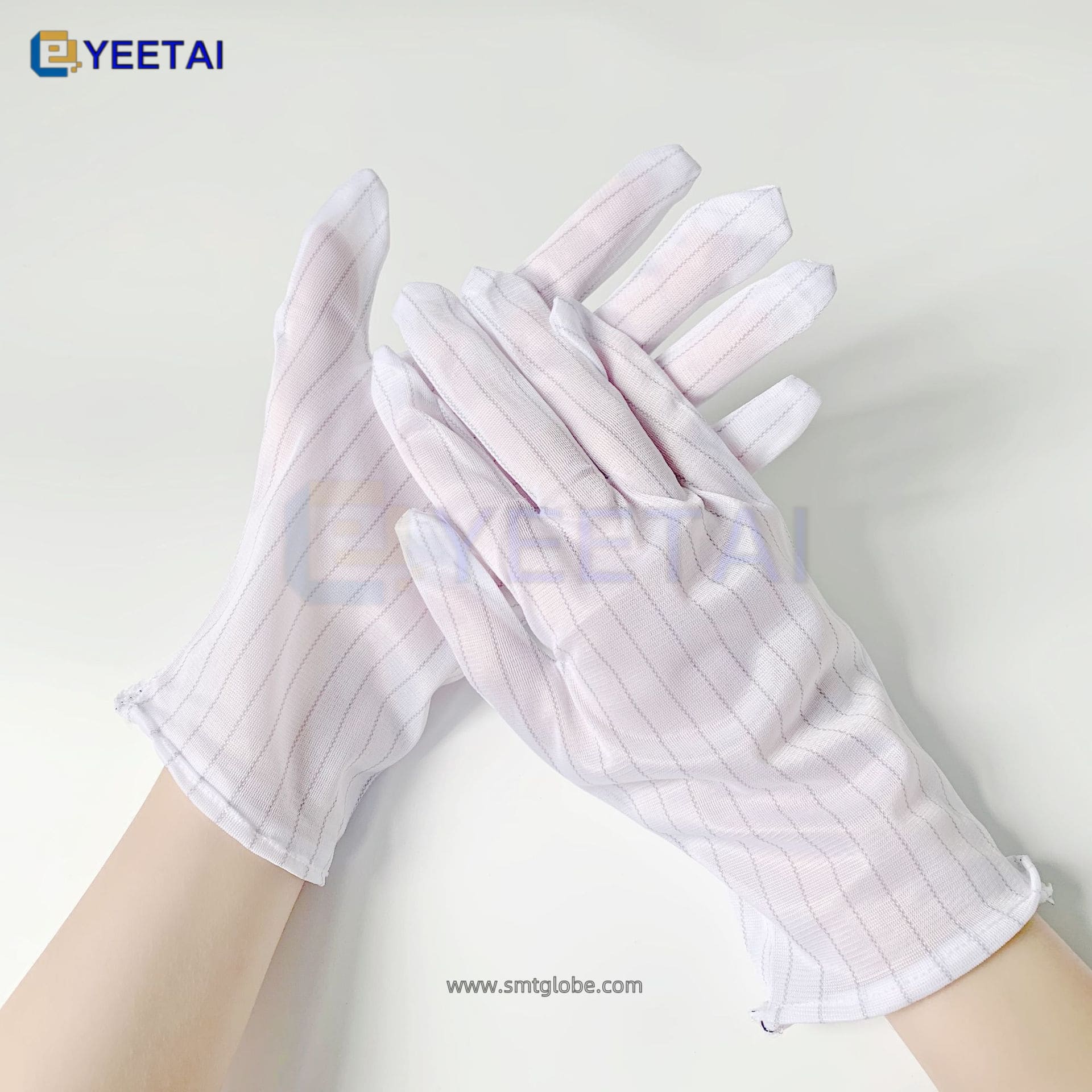
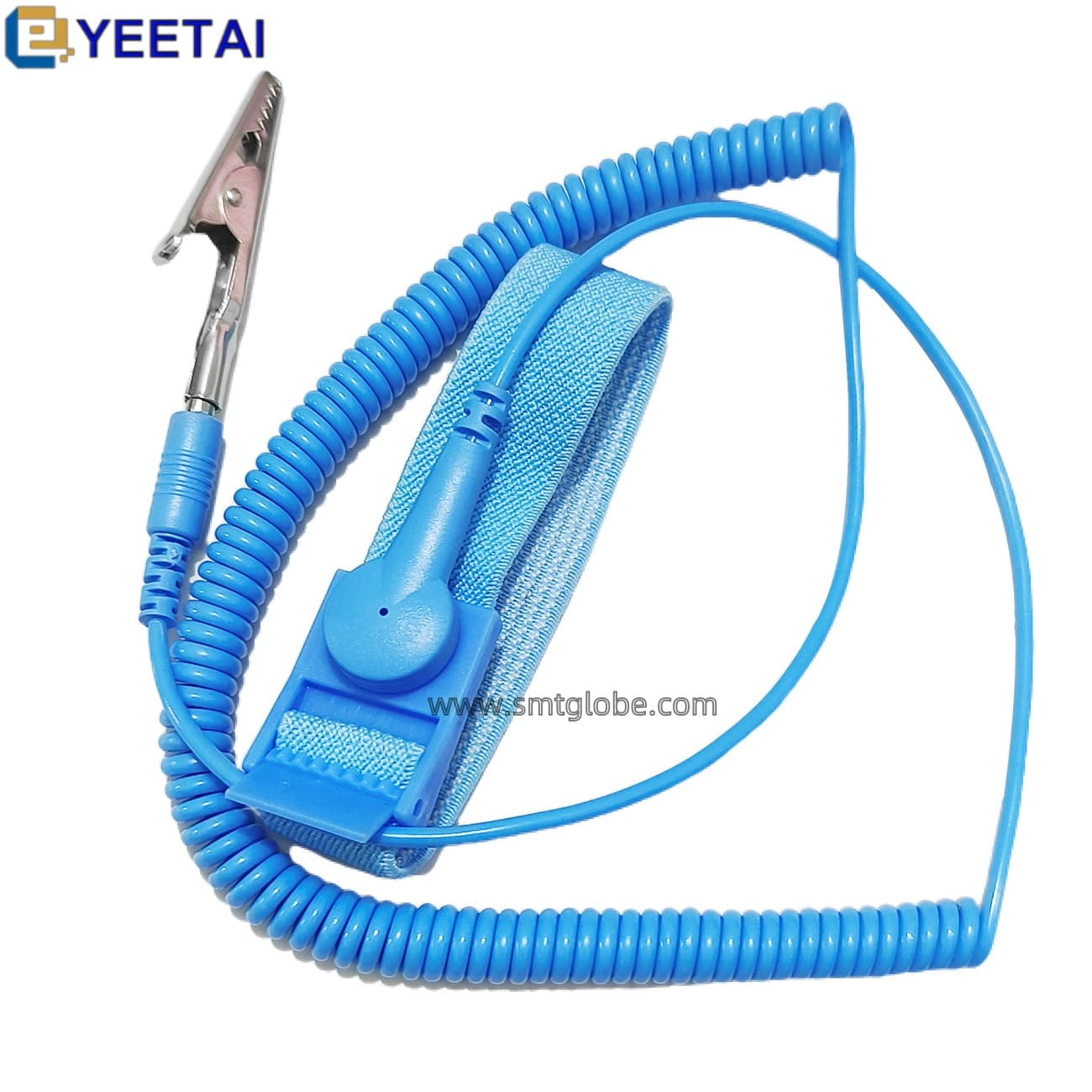




Enhance Your Anti-Static Strategy with Our Products
At YEETAI, we specialize in high-quality anti-static products designed to protect your electronics from ESD damage. Our offerings include:
- Anti-Static Foams and Bags: Protect components during storage and transport.
- Ionizing Air Blowers (ESD ionizer): Help neutralize static charges in your working environment.
- Anti-Static Tools and Accessories: From mats to packaging solutions, we have everything you need for effective static control.
- ESD PCB storage trolley
- ESD magazine rack
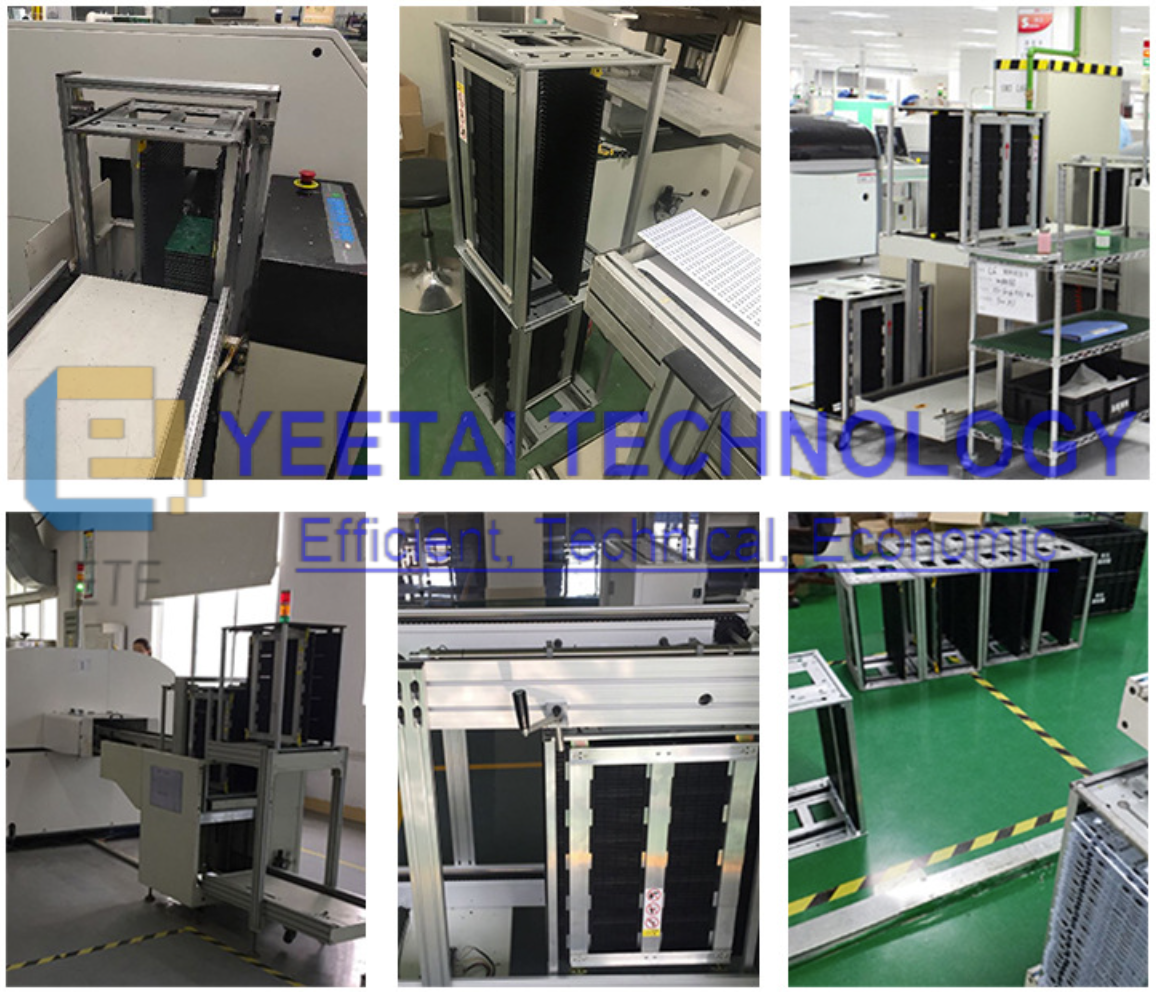



Conclusion
Understanding static electricity and implementing effective anti-static measures is vital to protecting your electronics. If you’re looking for reliable anti-static solutions, explore our product range at www.smtglobe.com or contact us directly at info@smtglobe.com. Let us help you safeguard your operations from the hidden dangers of static electricity!