Basic Requirements for Electrostatic Prevention in PCBA Electronic Factories
I. Basic Principles of Static Electricity Protection
a. Suppress the accumulation of static charges;
b. Quickly, safely, and effectively eliminate any static charges that have already developed.
II. Electrostatic Protection Work Area
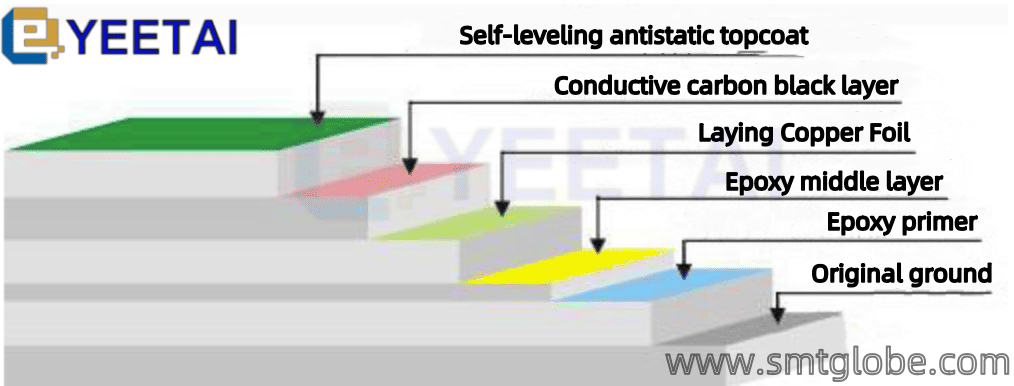
- Flooring Materials
a. Direct use of wooden floors, carpets made of wool, hemp, synthetic fibers, or ordinary vinyl flooring is prohibited.
b. Flooring made of static conductive materials should be used, such as anti-static raised flooring or laying anti-static mats over regular flooring, with effective grounding.
c. Specially treated terrazzo flooring is permitted, provided that grounding mesh is laid beforehand, carbonization is applied, or anti-static agents are sprayed on the floor.

2. Grounding
a. The electrostatic protection system must have an independent and reliable grounding device, with a grounding resistance typically less than 10Ω, and the grounding method must comply with the requirements of GBJ97.
b. The anti-static ground wire must not be connected to the power supply neutral wire and must not share grounding with lightning protection.
c. A three-phase five-wire power supply system should be used, where the ground wire can serve as an anti-static ground wire (but the neutral and ground wires must not be mixed).
d. Grounding Main Line
- The cross-sectional area of the grounding main line should not be less than 100 mm²; the cross-sectional area of branch lines should not be less than 6 mm²; grounding wires for equipment and work tables should use multi-stranded insulated conductors with a cross-sectional area of at least 1.25 mm², preferably using green-yellow colored wires.
e. Connection Method
- The connection method for the grounding main line should employ welding.
f. Electrostatic Equipment Connection
- Terminals for connecting anti-static equipment must ensure reliable contact, be easy to install and disassemble, and permit the use of various clamp-style connectors, such as alligator clips, sockets, etc.
3. Ceiling Materials
- Ceiling materials should be made of anti-static type materials. Generally, gypsum board products are allowed, while ordinary plastic products are prohibited.
4. Wall Materials
- Wall materials should use anti-static wallpaper. Generally, gypsum or lime-based coatings are allowed, while ordinary wallpapers and plastic wallpapers are prohibited.
5. Humidity Control
a. The relative humidity in the electrostatic protection work area should be no less than 50%.
b. Humidification devices may be used to spray agents or water to increase environmental humidity, provided that it does not adversely affect the products.
c. The humidity in computer rooms should comply with the relevant regulations in GB2887, and similar rooms should also adhere to these regulations.
6. Area Boundaries
- The boundaries of the electrostatic protection work area should be clearly marked, with warning signs prominently displayed. These signs should comply with GJB1649 regulations, and ionized air shower devices should be installed at the entrance of the work area.
7. Prohibition of Static Charge Sources
- The use and contact with items that can easily generate static charges are prohibited within the electrostatic protection work area (as listed in the table below):
| Prohibited Items |
| Paint or varnished surfaces |
| Ordinary plastic laminate |
| Plain vinyl and resin surface flooring |
| Polished or waxed wooden floors |
| Ordinary vinyl resin workwear, hats, shoes |
| Ordinary polyester, synthetic fibers, and nylon fabric |
| Plastic and ordinary rubber-soled shoes |
| Ordinary plastic boxes, racks, bottles, trays |
| Paper products |
| Ordinary foam and general mobile tools |
| Compressors, spraying equipment, and evaporators |
8. Electrostatic Protection Facilities for Electronic Products
1. Electrostatic Safety Workbench
a. The electrostatic safety workbench is a fundamental component of the electrostatic protection area. It includes a workbench, anti-static desk mat, wrist strap connectors, and grounding wires.
b. The anti-static desk mat should have at least two wrist strap connectors—one for the operator and another for technical staff, inspectors, or other personnel.
c. When necessary, an ionized air static eliminator should be equipped on the electrostatic safety workbench.
d. It is prohibited to store items that easily generate static electricity, such as plastic boxes, rubber, cardboard, glass, etc., on the electrostatic safety workbench. Drawings and documents should be kept in anti-static folders.
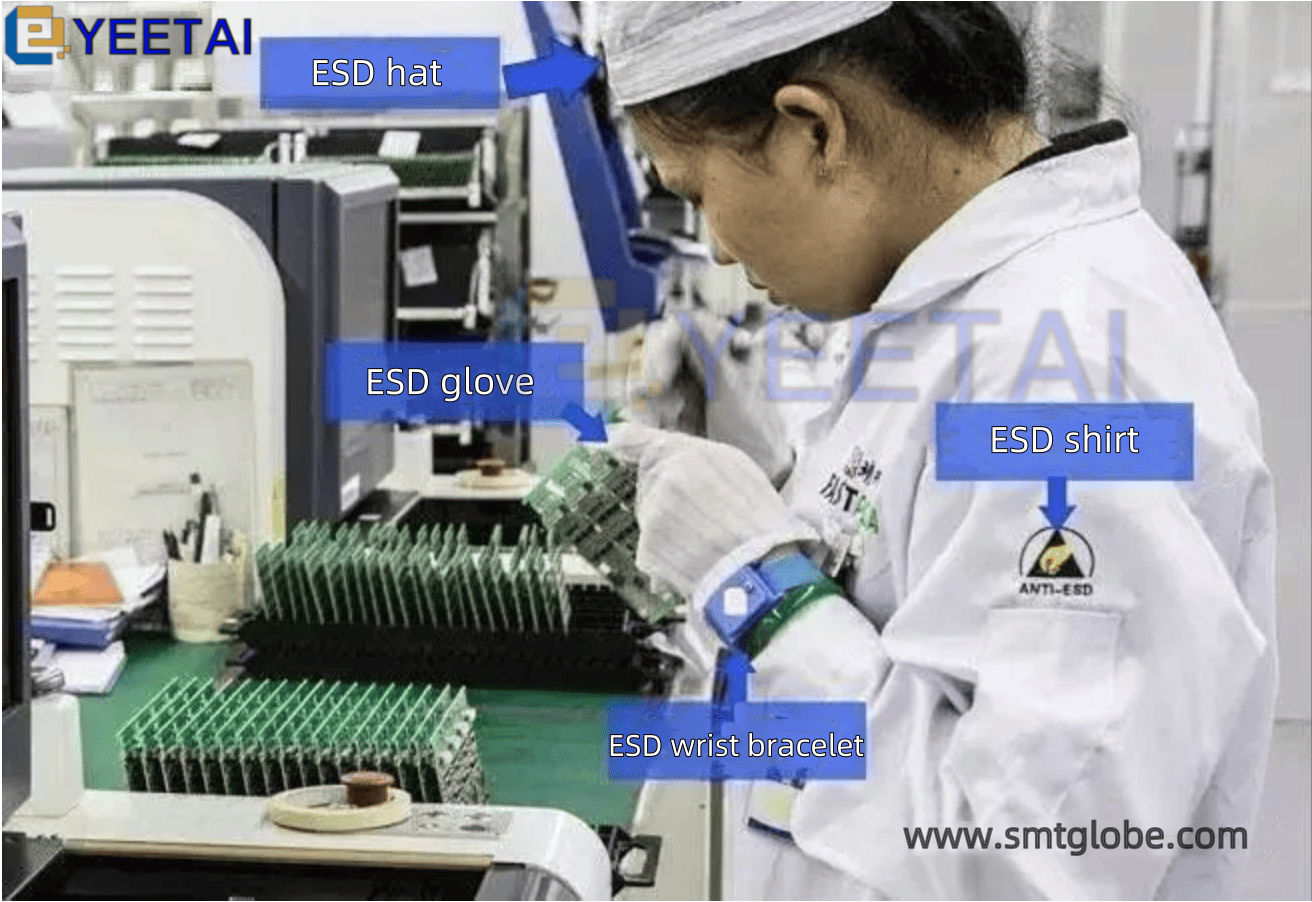
2. Anti-static Wrist Straps
- All personnel who directly handle static-sensitive devices must wear anti-static wrist straps, which should maintain good contact with the skin. The wrist straps must be non-irritating and non-allergenic, with a grounding resistance value between 10^6 to 10^8 Ω.
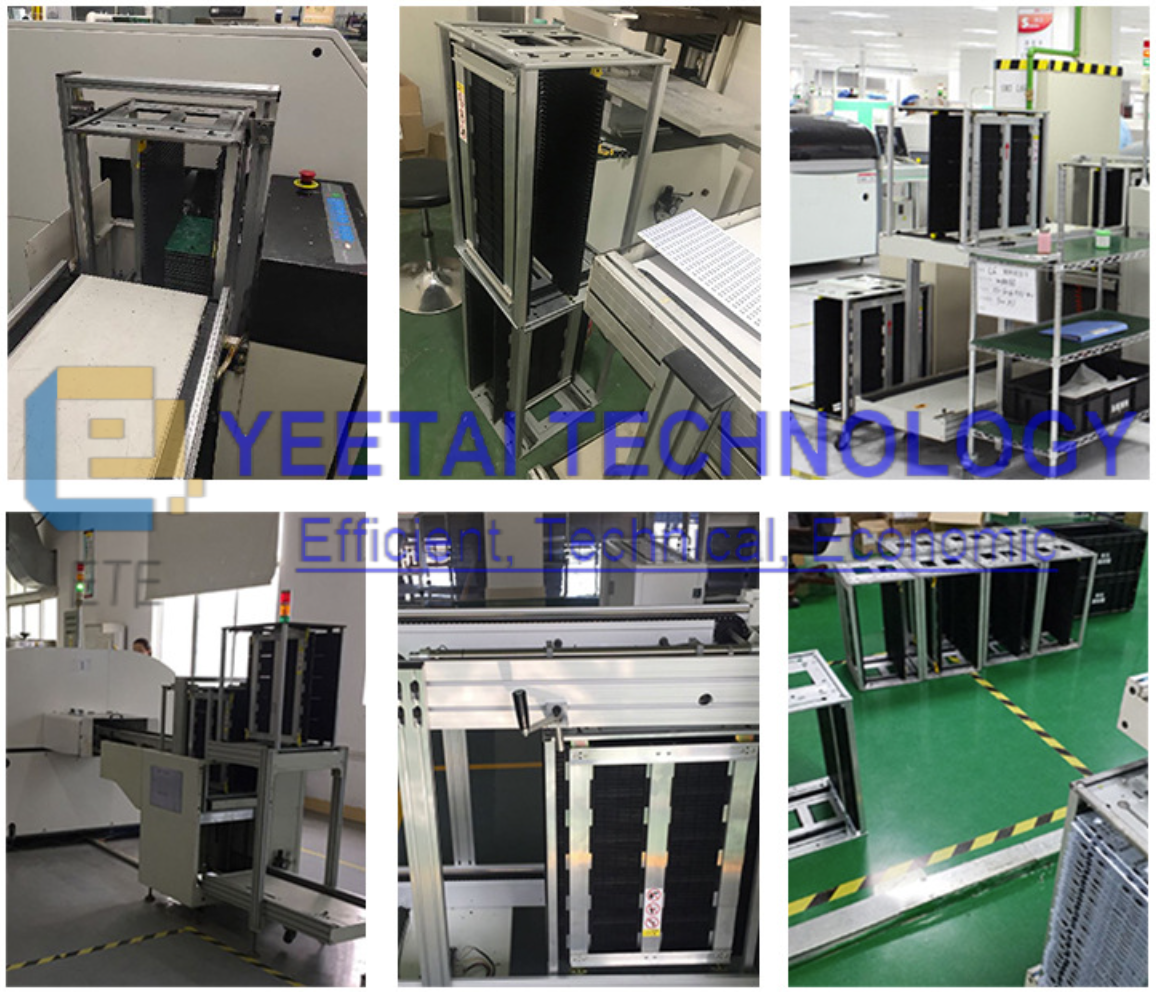
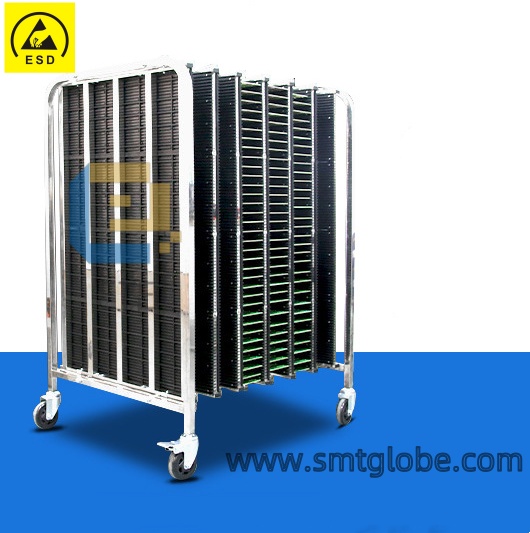
3. Anti-static Containers
- During the research and production of electronic devices, all containers for storing and transferring SSDs (component bags, transport boxes, PCB racks, component storage boxes, etc.) must have electrostatic protection capabilities. Metal and ordinary plastic containers are not allowed. When necessary, transport boxes for storing components should be grounded.
4. Ionized Air Static Eliminators
- Ionized air static eliminators should be used to eliminate static charges on the surfaces of insulating materials.
5. Anti-static Work Clothes
a. Personnel entering the electrostatic protection area or handling SSDs should wear anti-static work clothes, which must comply with GB12014 standards.
b. In environments with relative humidity greater than 50%, pure cotton products may be utilized for anti-static work clothing.
6. Anti-static Work Shoes
- Personnel entering the electrostatic protection area or handling SSDs should wear anti-static work shoes that comply with GB4385 regulations. Regular shoes are generally allowed but should be paired with conductive shoe straps or heel bands.
7. Anti-static Transport Trolleys
- When transporting SSDs or components containing SSDs, transport trolleys with anti-static properties should be used.
8. Static Protection Operating Specifications
1. Purpose
- Clearly define the electrostatic operation specifications for equipment, documents, materials, and other items across all departments.
2. Scope
- These operating specifications apply to all departments.
3. Specific Operational Requirements:
3.1 Design Department
3.1.1 Product designers must develop an electrostatic discharge control outline during product development to ensure electrostatic discharge protection for the product.
3.1.2 During the design phase, potential issues of static discharge failure or performance degradation should be analyzed, prompting design personnel to implement protective measures on circuits and to mark static-sensitive components with the symbol ф on design drawings for focused electrostatic control.
3.2 Procurement Department
3.2.1 For externally purchased static-sensitive components, suppliers are required to provide anti-static protection and labels for electrostatic discharge-sensitive components per specifications.
3.3 Quality Control Department
3.3.1 When the inspection team checks delivered static-sensitive components against the order list, they must verify the presence of protective packaging and product markings, rejecting any non-compliant products.
3.3.2 Inspections of static-sensitive components should be conducted under conditions that ensure electrostatic discharge protection (consistent with the “Component Anti-static Operation Regulations”).
3.3.3 The Quality Engineering (QE) department is responsible for supervising electrostatic inspection points and reporting any non-compliant processes to department heads for timely resolution. Losses incurred due to improper resolution will be the responsibility of the relevant departments, who will face penalties. They will also oversee the production and publication of electrostatic protection bulletin materials.
3.3.4 An anti-static training plan should be established, initiated by the Quality Control Department, in conjunction with the Education Department and the Process Department, to ensure that all personnel handling static-sensitive components receive the necessary training and achieve proficiency.
3.4 Human Resources Department
3.4.1 Organize training sessions on electrostatic knowledge for employees, followed by assessments.
3.5 Production Management Department
3.5.1 Responsible for providing data and training related to electrostatic protection.
3.6 Equipment Department
3.6.1 Grounding wires should be inspected weekly to ensure each connection is free from oxidation and properly grounded. Inspection records must be maintained.
3.6.2 Basic production equipment, such as assembly lines, wave soldering machines, and aging lines, should be inspected weekly to confirm that there are no electric leaks and that grounding is adequate. Records of the inspections should be documented.
3.7 PCBA Workshop
3.7.1 All operations involving static-sensitive components must be conducted at electrostatic safety workbenches. Components without anti-static packaging are not allowed in the production area. Components lacking anti-static packaging should be treated to eliminate static before entering the static-sensitive work area.
3.7.2 All tools, fixtures, and equipment that do not possess anti-static capabilities must be placed on anti-static mats.
3.7.3 External personnel entering the site without anti-static measures are prohibited from touching components.
3.7.4 All equipment in the production area must implement electrostatic protection measures.
3.7.5 During manual soldering, anti-static low-voltage soldering irons must be used.
3.7.6 When cleaning sensitive components after soldering, plastic brushes are not permitted; only anti-static brushes should be used.
3.7.7 Employees must ensure that their anti-static wrist straps have good contact with the skin. The resistance values for the wrist strap system, anti-static desk mats, and anti-static floor mats should be within 1 MΩ ± 10%. This should be measured daily by the workshop technician or line leader using a qualified multimeter, with inspection records maintained.
3.7.8 All charged tools, instruments, and equipment must be properly grounded. This should be measured weekly on Mondays by the workshop technician or line leader using a qualified multimeter, with inspection records kept.
3.7.9 Employees who have not undergone anti-static training are not allowed to assemble components containing electrostatic discharge-sensitive devices. Employees wearing synthetic fiber clothing should avoid contact with static-sensitive components.
3.7.10 It is prohibited to stack electrostatic discharge-sensitive components together; components must not touch each other. Circuit boards with sensitive components should not be stacked but placed separately in anti-static containers.
3.7.11 When testing or repairing without wearing an anti-static wrist strap, personnel must touch a grounded metal surface to discharge any static electricity. Individuals not taking anti-static measures are strictly prohibited from touching static-sensitive components or circuit boards.
3.8 Warehouse
3.8.1 When transporting components with leads, conductive foam materials should typically be used to prevent high potential differences between component leads. For dual in-line packaged components, anti-static dissipative tubes are commonly used during bulk transport. For circuit board components located outside the electrostatic discharge protection zone, they should be placed in anti-static shielding bags or conductive transport boxes. Some packaging bags are made from conductive materials, ensuring that all components remain at the same potential under stable conditions while dissipating any static charge that may accumulate on the bag. This method is not suitable for circuit boards with batteries; in such cases, packaging bags lined with anti-static dissipative materials and an outer layer of conductive material should be used. Though these bags are more expensive, they provide excellent protection for both powered and unpowered components.
Similarly, conductive boxes containing fixed circuit boards should not be used with powered circuit boards that have exposed connectors on the edges.
Management of Electrostatic Protection Facilities in the Production Area
- Electrostatic Safety Workbench: Composed of a workbench, anti-static desk mat, wrist strap connectors, and grounding wires.
- Anti-static Desk Mat: Should have at least two wrist strap connectors—one for the operator and another for technical staff or inspectors.
- Storage Restrictions: The electrostatic safety workbench should not have plastic boxes, rubber, cardboard, glass, or other items that easily generate static. Drawings and data should be stored in anti-static document bags.
- Anti-static Wrist Straps: Personnel directly handling static-sensitive devices must wear anti-static wrist straps with good contact to the skin. The wrist strap system’s resistance to ground should be 1 MΩ.
- Anti-static Containers: Component storage bags, transport boxes, and PCB racks in the production area must have electrostatic protection capabilities. Metal and ordinary containers are not allowed, and all containers must be grounded.
- Anti-static Work Clothes: Personnel entering the electrostatic work area or handling SMD components must wear anti-static work clothes, particularly in dry environments with humidity less than 50% (e.g., winter). The fabric must meet relevant national standards.
- Anti-static Work Shoes: Personnel entering the work area must wear anti-static shoes. Those wearing regular shoes should use conductive shoe straps, anti-static shoe covers, or heel bands.
- Conveyor Belts and Drive Shafts: These should be equipped with anti-static grounding brushes and supports.
- Ionized Air Static Eliminators: Should be used on conveyor belt surfaces.
- Grounding for Tools and Instruments: Assembly fixtures, testing fixtures, soldering tools, and various instruments used in the production area must have proper grounding.
- Entrance Testing: An anti-static testing station should be installed at the entrance of the production area, and all personnel entering must undergo electrostatic testing, with only those passing allowed to enter the site.


We also produce other ESD products.