What is a SMT warehousing AGV robot? When we talk about warehousing robots, the most mentioned is AGV. AGV refers to Automated Guided Vehicle, which is a component of the Automated Guided Vehicle Systems (AGVS) in warehousing robot systems. The AGVS includes infrastructure, data transmission equipment, devices for positioning and determining location, guidance control systems, and several Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), and it is a ground-based material handling system whose main task is material transportation, not personnel.
Warehousing robots are classified into operator-controlled and automatic control categories based on whether they are controlled by operators: operator-controlled can be further divided into direct operator control and operator remote control; automatic control can be divided into predefined path and non-predefined path.
We are mainly discussing AGVs with predefined paths, which are ground-based material handling devices controlled and guided automatically by a non-contact guidance system.
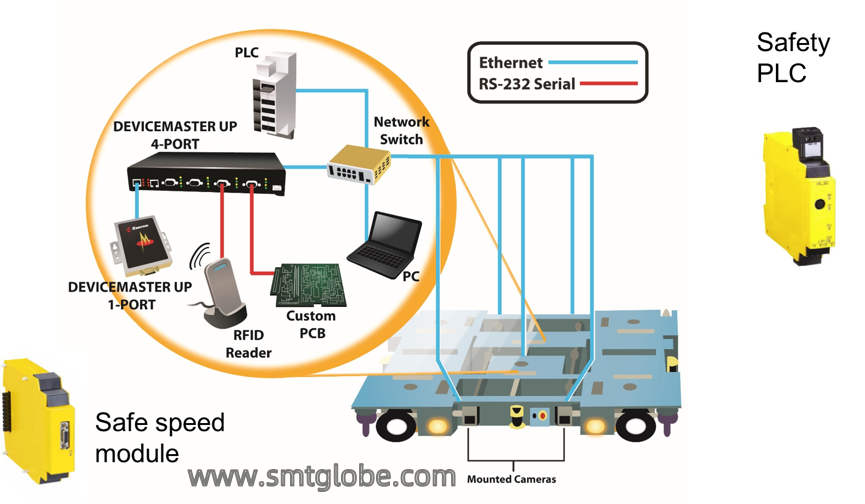
They are mainly composed of safety devices (emergency stop buttons, laser radar, safety PLC, safety speed modules), control devices, load handling devices, drive devices, batteries, and motors.
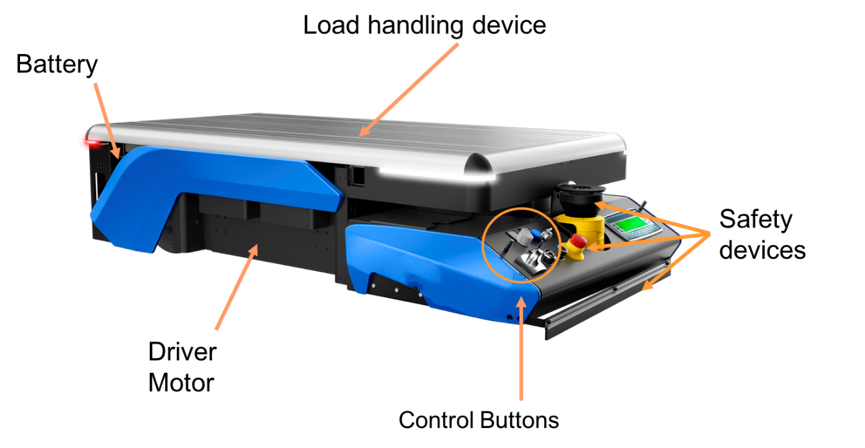
In terms of control, this includes functional control (such as command parsing, wireless communication, navigation data processing, image processing, etc.), power control (such as power supply, charging control, etc.), and safety control (such as obstacle detection, speed and steering control, etc.).
European Safety Requirements The applicable directives for SMT warehousing AGV mainly include mechanical directives, electromagnetic compatibility, and wireless directives. If used in explosive atmospheres, it should also comply with explosion protection directives.
The applicable European standards for SMT WAREHOUSING AGV mainly include EN 1175-1 and EN 1525, and their safety requirements can be divided into three parts: mechanical, electrical, and control.
- Mechanical safety requirements, including design requirements for load handling devices, stability requirements, mechanical braking safety requirements, etc.
- Electrical safety requirements, including charging systems such as batteries, battery connectors, charging stations, motors, contactors, wiring, electrical protection, testing, etc.
- Control safety requirements, including safety device requirements (such as emergency stop, warning devices, personnel detection devices, etc.), control safety requirements (such as charging control, handling control, steering control, speed control, travel control, etc.), as well as low voltage, parameter errors, and shell faults.
III. Six Major Safety Issues During the product certification process for domestic SMT WAREHOUSING AGVs, TUV Rheinland found that many companies, due to insufficient understanding of regulations, designed products that did not meet European safety requirements, making it difficult to successfully export overseas. These problems mainly occur in the following six major safety requirements:
- Mechanical braking system
1.1 Safety requirements:
a) SMT WAREHOUSING AGVs should be equipped with a mechanical braking system.
b) Functional requirements: First, use power-off braking; second, work when there is a power interruption or malfunction; third, work when the vehicle loses speed or steering.
c) Braking requirements:
♣ The braking device should ensure that the SMT WAREHOUSING AGV and its maximum allowable load can be maintained on the manufacturer’s specified working slope without slipping.
♣ Considering the load, speed, friction, slope, and wear, the braking system should be able to stop the SMT WAREHOUSING AGV within the detection range of the laser radar. ♣ When the vehicle is in manual mode, the brake should meet the requirements of ISO 6292.
1.2 Existing problems:
Domestic SMT WAREHOUSING AGVs generally do not have a mechanical braking system, with most using electronic brakes, and some not even having a braking system, let alone meeting the action and braking requirements.
- Stability
2.1 Safety requirements:
a) Load handling device:
♣ It should be designed so that the load cannot move from the manufacturer’s specified position in any operating mode, including emergency stops and loading and unloading.
♣ If the lifting height exceeds 1.8 meters, it should be verified by testing.
♣ If the lifting height does not exceed 1.8 meters, it can be verified by calculation.
b) Stability requirements: The stability of the SMT WAREHOUSING AGV should be ensured in all operating positions during load handling and travel processes (including emergency stops).
c) Safety-related parts of the control system: If used for load handling, the control system faults for speed control and steering control may lead to stability loss, and these safety-related parts of the control system should comply with ISO 13849-1:2015: Cat.2.
2.2 Existing problems:
Currently, most handling devices mainly rely on friction to maintain the relative position relationship between the shelf and the SMT WAREHOUSING AGV. In emergency situations, once the emergency stop button is pressed, the shelf is likely to tilt or become unstable. Most SMT WAREHOUSING AGVs are not equipped with safety PLCs or safety relays, and the performance level requirements of safety-related parts of the control system have not been considered, let alone met.
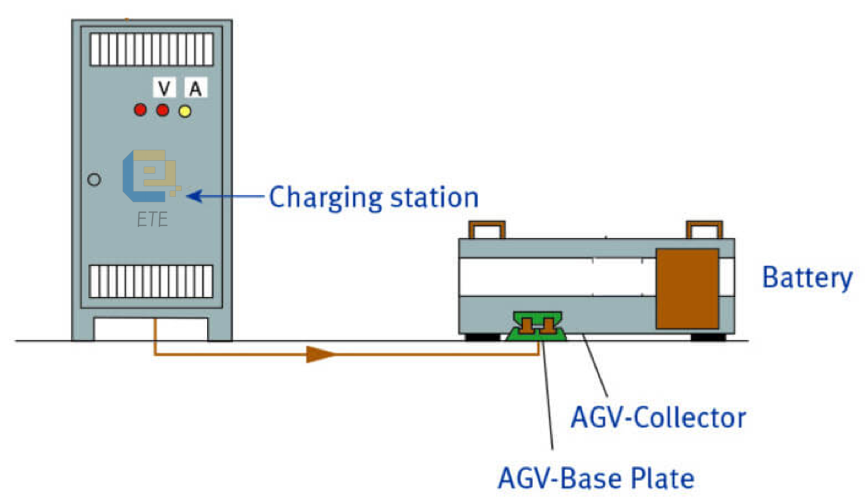
- Charging system Image
3.1 Safety requirements:
a) Charging connection:
a. It should prevent accidental contact with the charging connection on the SMT WAREHOUSING AGV and the charging station.
b) Automatic charging system should be designed to:
♣ Only start the charging connection when the SMT WAREHOUSING AGV is connected to the charging system.
♣ Close the charging connection when the vehicle leaves the charging system.
♣ The safety parts of the charging system should comply with ISO 13849-1:2015: Cat.1.
b) Battery: ♣ Lead-acid and alkaline (nickel-cadmium or nickel-iron) batteries should comply with the requirements of EN 1175-1 5.1.
♣ For other types of batteries, they need to meet the corresponding standard requirements. c) Battery connector: Should comply with the relevant requirements of Appendix A of EN 1175-1.
3.3 Existing problems:
a) Personnel detection devices should be able to detect the following specimens at least:
♣ Specimen with a diameter of 200mm and length of 600mm, located at any position along the SMT WAREHOUSING AGV path or the truck path and forming a right angle with the paths.
♣ Specimen with a diameter of 70mm and a height of 400mm, placed vertically within the SMT WAREHOUSING AGV path. d) Personnel detection devices (e.g., buffers) should not cause harm to personnel.
In addition, the following should be met:
♣ Diameter 200mm, length 600mm: The triggering force of this specimen should not exceed 750 N;
♣ Diameter 70mm, height 400mm: The triggering force of this specimen should not exceed 250 N; the force when the buffer is compressed from maximum speed and load to the stop position should not exceed 400N. e) Safety-related parts of the control system: Personnel detection device’s safety-related components should comply with ISO 13849-1:2015: Cat.3;
4.2 Existing Problems:
♣ There are blind spots in the detection, which do not cover the entire width of the SMT WAREHOUSING AGV or the shelves;
♣ The SMT WAREHOUSING AGV and cargo may come into contact with personnel, even crush or collide with them;
♣ Safety-related parts of the control system do not meet the requirements of ISO 13849-1:2015: Cat.3;
5. Emergency Stop
5.1 Safety Requirements:
a) Emergency stop device: ♣ The actuator of the emergency stop device should be easily visible from both ends and sides of the SMT WAREHOUSING AGV, and identifiable and accessible. In the case of the SMT WAREHOUSING AGV carrying a load at the end, it should only be accessible from the other end;
♣ The buttons of the emergency stop device should be red, with a yellow background;
b) Emergency stop function:
♣ A class 0 (power-off) emergency stop device complying with EN 13850 standard should be provided;
♣ Cut off the dangerous power supply of all moving parts;
♣ It should be able to interrupt the maximum normal current by one of the following methods (including the starting current of the motor):
- Below 96V (including 96V), the battery connector defined in Range1 of Appendix A can be used; battery connectors above 96V should not be used for emergency shutdown;
- Manual isolating devices, at least one pole should be disconnected;
- Manual operation of control switches, cutting off the power supply of the contactor coil; simultaneously cutting off the power circuit of the switch (e.g., inverter or controller of a separate motor); c) Safety-related parts of the control system: The safety-related components of the emergency stop device should comply with ISO 13849-1:2015: Cat.3;
- 5.2 Existing Problems:
- ♣ The installation position of the emergency stop device is unreasonable and not easily accessible from both ends and sides;
- ♣ Lack of a contrasting color for the emergency stop button;
- ♣ The emergency stop function does not comply with standard requirements, class 0 stop is not used, and the dangerous power supply of all moving parts is not cut off;
- ♣ Safety-related parts of the control system do not meet the requirements of ISO 13849-1:2015: Cat.3;
- Safety-related parts of the control system
Welcome to our website: www.smtglobe.com for more SMT WAREHOUSING AGV information.