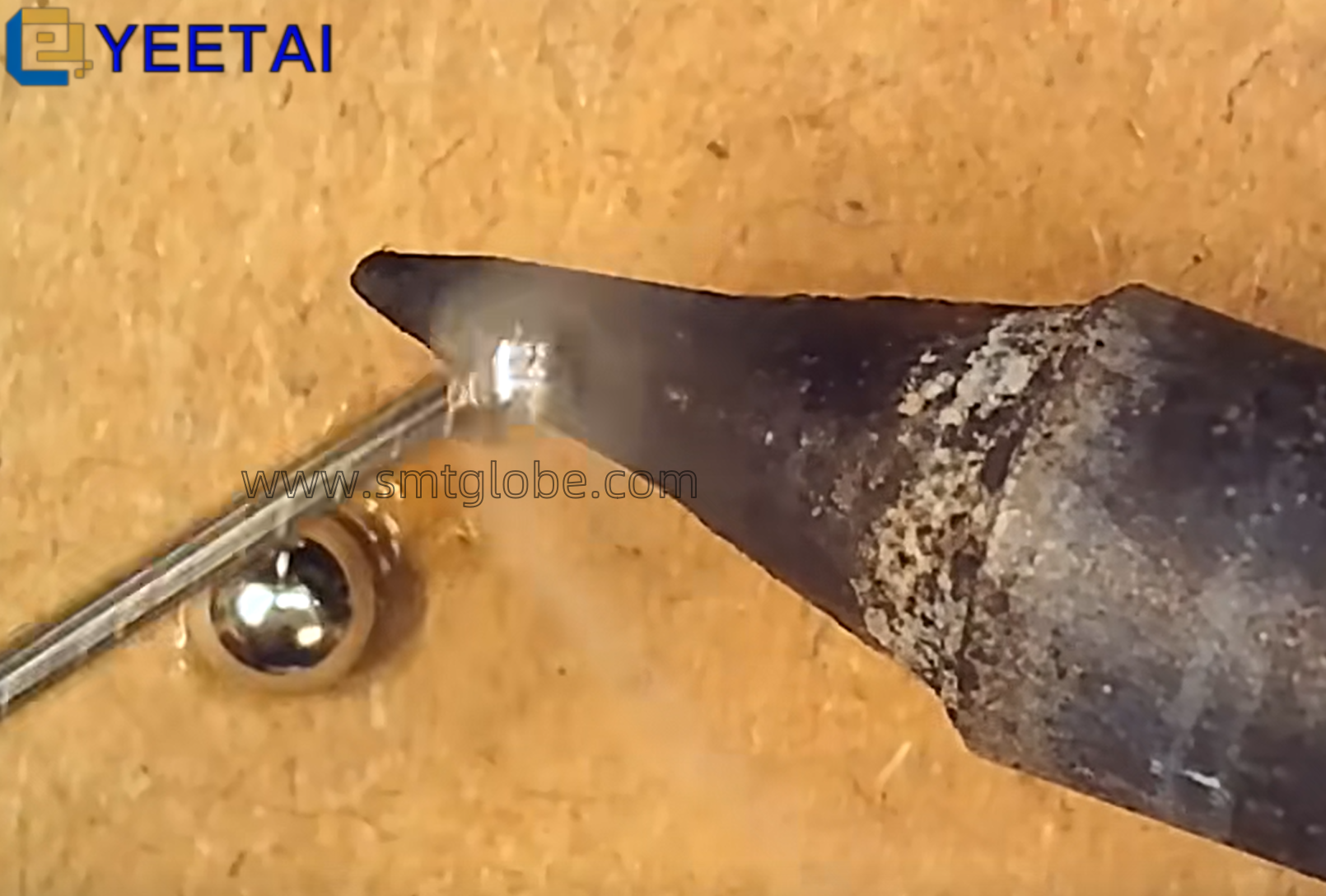
The functionality of SMT (Surface Mount Technology) feeders is crucial for maintaining efficiency in electronic assembly processes. Common problems with these feeders can be categorized into three primary areas: hardware issues, communication problems, and power supply issues. Below, we will delve into each category, providing insights and solutions.

1. Hardware Issues
One of the leading causes of malfunction in SMT feeders is improper usage or other hardware-related issues. It’s essential to refer to relevant documentation when troubleshooting hardware problems to ensure proper operation.
2. Communication Problems
a. IC Burnout on Circuit Boards
- Cause: Overvoltage or short circuits during feeder operation can lead to IC (Integrated Circuit) damage.
- Solution: Replace the damaged circuit board and reset the relevant parameters.
b. Communication Connector Issues
- Cause: Prolonged use can subject communication connectors to physical stress, resulting in damaged pins or foreign objects obstructing normal communication.
- Solution:
- Inspect the connector for foreign objects and remove any debris found.
3. Power Supply Issues
a. Feeder Not Receiving Power
- Cause: Issues in the power supply system, including plugs, power switches, or circuit board fuses.
- Solution:
- Check for any debris in the SMT feeder’s communication connector and inspect for any missing pins.
- Verify the status of limit switches, using alternative methods to troubleshoot if necessary.
- Check the circuit board fuses for any blown fuses—while this is rare, alternative testing can help confirm functionality.
b. Button Indicator Lights Not Illuminating
In some instances, the button indicator lights may not turn on, which can be mistaken for a power issue. To clarify:
- Utilize a new flat cable to test if the button is functioning correctly, helping streamline the troubleshooting process.
c. Feeder Modes
- When the sixth jumper is set to ON, the feeder operates in low-speed mode. Switching the jumper to OFF reverts the feeder to normal operation.
Using Feeder Check Software
The Feeder Check software provides critical information regarding the feeder’s performance:
- If the Serial Number within the red box does not match the serial number on the feeder, it is necessary to rewrite it. Click OK and follow the interface prompts to ensure the serial number matches; confirm by clicking Update.
- Notably, discrepancies between the mainboard information and the barcode information can lead to erroneous feeder readings, resulting in downtime. When a new, unopened feeder is received, use the Feeder Check software to assess feeder speed.
- Feeding Speed indicates the operational speed of the feeder.
After replacing a circuit board, it is critical to set the appropriate feeder type, as discrepancies can lead to data mismatches. If NXT Trace fails to read the feeder, it may significantly hinder production; thus, adjustments to the feeder type can be performed using jumper settings.
Conclusion
Understanding the common issues associated with SMT feeders—hardware problems, communication challenges, and power supply concerns—can significantly enhance the operational efficiency of electronic assembly processes. Proper troubleshooting and maintenance ensure smooth operation and minimize downtime in production.
At YEETAI, we produce all kinds of feeder to upgrade SMT machines.