All types of SMT AGV Robots are presented here.
Welcome to know more about SMT AGV at www.smtglobe.com
Or contact info@smtglobe.com for help.
- Infiltration type: It infiltrates the bottom of the material cart, automatically attaches and detaches to deliver and retrieve materials.
- Traction type: It pulls the material cart through automatic attachment and detachment mechanisms at the rear.
- Self-unloading type: Equipped with a platform, it interfaces with materials using rollers, belts, or other methods.
- Lifting type: The platform can automatically lift materials and operate in sync with the assembly line.
- Forklift type: It uses an open forklift for material handling.
Advantages:
- High degree of automation: Controlled by computers, electronic devices, magnetic induction sensors, laser reflectors, etc. When a workshop section requires auxiliary materials, the computer terminal receives input from the staff, sends the information to the central control room, and professional technicians send instructions to the AGV robot to deliver the materials to the designated location.
- Automated charging: When the AGV robot’s battery is running low, it sends a request to the system for charging (a predefined threshold set by technicians). Upon system approval, it automatically queues up for charging at the designated location. Additionally, the AGV robot’s battery has a long lifespan (over 2 years).
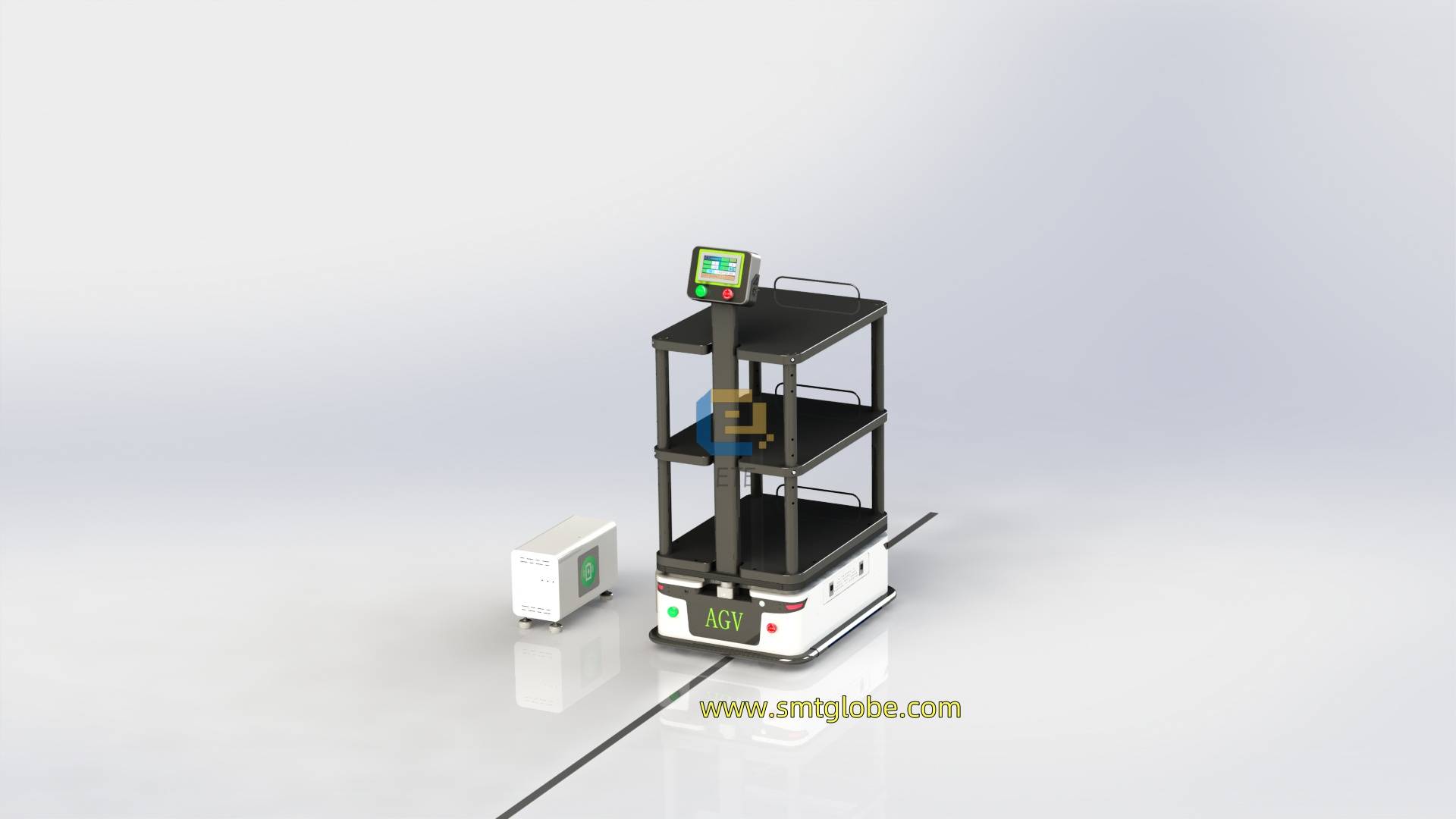

AGV Robot Guidance Methods
1. Electromagnetic Guidance
- How it Works: Metal wires are embedded along the AGV robot’s path, carrying specific guidance frequencies. The robot recognizes these frequencies to navigate.
- Advantages:
- Discreet wiring.
- Resistant to pollution and damage.
- Simple and reliable guidance principles.
- Easy control and communication.
- Not affected by sound and light.
- Lower manufacturing costs.
- Disadvantages:
- Complex wire installation.
- Difficult to change or expand paths.
- Susceptible to interference from ferromagnetic materials.
- Limited to simple paths.
2. Magnetic Tape Guidance
- How it Works: Magnetic tape is placed on the surface instead of buried wires. The AGV robot uses magnetic induction signals for guidance.
- Advantages:
- Flexible paths that are easy to change or expand.
- Simple installation of magnetic tape.
- Disadvantages:
- Susceptible to interference from nearby metal objects.
- Mechanical damage can affect the tape.
- Once a task starts, the robot can only move along the fixed tape and cannot change tasks.
3. Magnetic Card Guidance
- How it Works: The travel area is divided into coordinate sub-regions using positioning blocks. The robot counts these sub-regions using magnetic strip tag cards to navigate to target stations.
4. Laser Guidance
- How it Works: Precise laser reflectors are installed along the path. The AGV robot emits a laser beam and collects the reflected beam to determine its position and direction.
- Advantages: Provides accurate navigation through continuous calculations.
5. Color Tape Guidance
- How it Works: Color tapes are painted or pasted along the travel path. The robot uses a camera to process the color tape image signals for guidance.
- Advantages:
- Easy to install on road surfaces.
- Good flexibility and low cost.
- Disadvantages:
- Susceptible to pollution and damage.
- Requires a clean environment for reliable operation.
- Lower accuracy compared to other methods.
6. Mobile Phone Remote Control
- How it Works: The robot’s movement can be controlled through a mobile app. Users download the app to manage the robot’s tasks and navigation.

AGV ROBOT’s Basic Applications
Manufacturing Industry SMT AGV Robots shine in manufacturing production lines, efficiently, accurately, and flexibly completing material handling tasks. Multiple SMT AGV Robots can form a flexible logistics handling system, with transport routes adjusted in real-time to align with production process changes, enabling a single production line to manufacture a dozen or more products, significantly enhancing production flexibility and competitiveness for enterprises. In 1974, Volvo Kalmar car assembly plant in Sweden adopted an automatic car assembly line using SMT AGV Robots as carriers to enhance transport system flexibility.
The assembly line, consisting of multiple SMT AGV Robots capable of carrying car bodies, reduced assembly time by 20%, decreased assembly failures by 39%, reduced investment payback time by 57%, and lowered labor by 5%. Currently, SMT AGV Robots are widely used in the manufacturing and assembly lines of major car manufacturers worldwide, such as General Motors, Toyota, Chrysler, and Volkswagen. In recent years, as a fundamental handling tool for Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems (CIMS), the application of SMT AGV Robots has extended to various industries including mechanical processing, household appliance production, microelectronics manufacturing, and tobacco, making production and processing the most widely applied field for SMT AGV Robots.
SMT Factories, Post Offices, Libraries, Port Terminals, and Airports In scenarios like SMT factories, post offices, libraries, port terminals, and airports, where there are significant variations in workload, high dynamics, frequent process adjustments, and a single handling process, SMT AGV Robots’ parallel operation, automation, intelligence, and flexibility characteristics effectively meet the handling requirements of these environments. Sweden started using SMT AGV Robots at the Stockholm post office in 1983, Japan at the Tama post office in 1988, and China at the Shanghai postal hub in 1990 to handle mail items. In the port of Rotterdam, the Netherlands, 50 SMT AGV Robots known as “yard tractors” handle repetitive tasks of transporting containers from the ship to warehouses several hundred yards away.
Tobacco, Pharmaceuticals, Food, Chemicals Industries like tobacco, pharmaceuticals, food, and chemicals, which have special requirements for clean, safe, and emission-free handling operations, also prioritize the application of SMT AGV Robots.
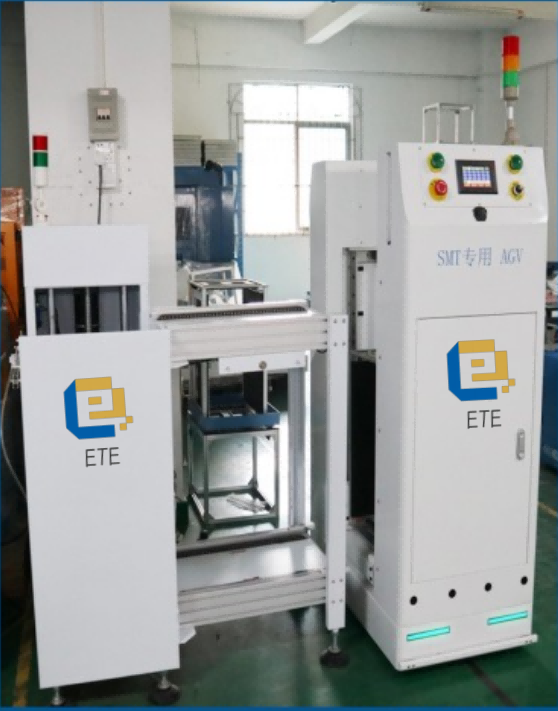

Welcome to know more about SMT AGV at www.smtglobe.com
Or contact info@smtglobe.com for help.