The maintenance of SMT feeders is a crucial aspect of their proper usage, necessitating a mandatory maintenance system to replace the reactive approach of repairing only when failures occur. This proactive strategy aims to minimize extensive disassembly and repairs. The maintenance of SMT feeders is guided by a preventive philosophy, organizing maintenance tasks based on their frequency into three distinct levels: Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 maintenance.
Level 1 Maintenance
Level 1 maintenance serves as the foundation for all technical maintenance activities. It is essential for technical management departments to prioritize the quality of Level 1 maintenance. This level is executed by specialized maintenance personnel and primarily focuses on cleaning, lubrication, and tightening. Key tasks include checking operational instruments, safety components, various valves, and the oil levels of lubricants.
Level 2 Maintenance
Level 2 maintenance for Yamaha SMT feeders centers on cleaning, inspection, adjustment, and calibration. This level is also carried out by professional maintenance staff. In addition to performing Level 1 maintenance tasks, technicians check the lubrication status of moving parts, clean various filters, verify the reliability of safety components, eliminate potential hazards, adjust the fit of wear-prone parts, assess the wear of rotating components, and calibrate operational and control instruments. This level of maintenance aims to extend the lifespan and maintain the technical performance of the SMT feeders.
Level 3 Maintenance
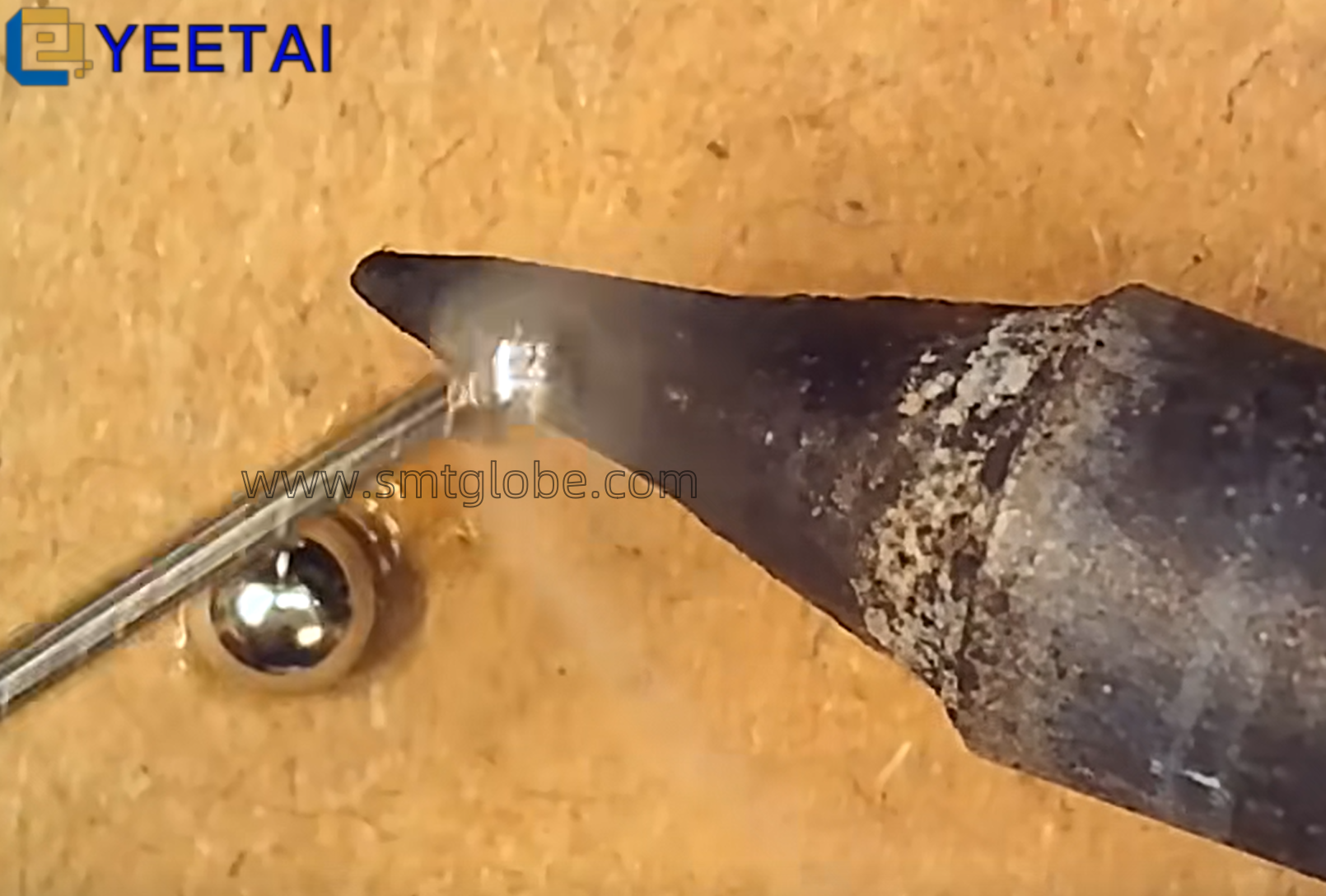
Level 3 maintenance focuses on disassembly, cleaning, inspection, and adjustment. This involves dismantling and cleaning gearboxes and electromagnetic speed controllers, removing dirt and carbon buildup, and inspecting components as needed. Technicians may also perform rust removal and repainting, as well as testing and inspecting electrical components of the SMT feeders. This comprehensive check ensures that all aspects of the feeder are functioning optimally.
Seasonal Maintenance
In addition to the three maintenance levels, there is a special category known as seasonal maintenance. Due to significant temperature variations between winter and summer, the working conditions of SMT feeders can change dramatically. Therefore, before entering these seasons, seasonal maintenance should be conducted in conjunction with Level 2 maintenance to prevent performance issues and component damage caused by temperature fluctuations.
Reporting and Documentation
In the event of a mechanical failure during production, it is crucial to promptly notify the team leader to contact maintenance personnel. A “SMT Feeder Maintenance Record” should be filled out, and after repairs, the equipment must be inspected by the user to ensure normal operation before resuming work.
Conclusion
Implementing a structured maintenance system for SMT feeders is vital for ensuring their reliability and efficiency in production. By adhering to the defined maintenance levels and conducting seasonal checks, manufacturers can significantly enhance the performance and longevity of their SMT feeders.
At YEETAI, we produce all kinds of feeder to upgrade SMT machines.