In the realm of SMT (Surface Mount Technology) assembly, enhancing production efficiency is a well-discussed topic, and one significant factor affecting this efficiency is component discard. Discard refers to instances when the pick-and-place machine’s nozzle fails to place components onto the PCB (Printed Circuit Board) and instead deposits them into a discard box. This can occur when the machine doesn’t pick up components correctly, resulting in wasted operational time. Discards can severely impact the overall production line’s efficiency and lead to issues such as incomplete products or shortages. Below, we share the causes of discards in SMT machines and effective improvement methods.
Causes and Solutions for Component Discards in SMT Assembly
1. Incorrect Nozzle Size
Cause Analysis: The nozzle size is not appropriately set for the component parameters. Generally, larger components might be mistakenly paired with nozzles that have a smaller aperture, leading to insufficient suction power to pick the component effectively, resulting in discards.
Solution: Adjust the machine parameters to select the appropriate nozzle corresponding to the size of the components being used.
2. Clogged Nozzle and Insufficient Air Pressure
Cause Analysis: A clogged nozzle or insufficient air pressure can cause the machine to pick components incorrectly or fail to pick them up altogether, leading to erroneous discard due to image recognition errors.
Solution: Regularly clean the nozzles and follow the equipment maintenance records to reduce operating failures.
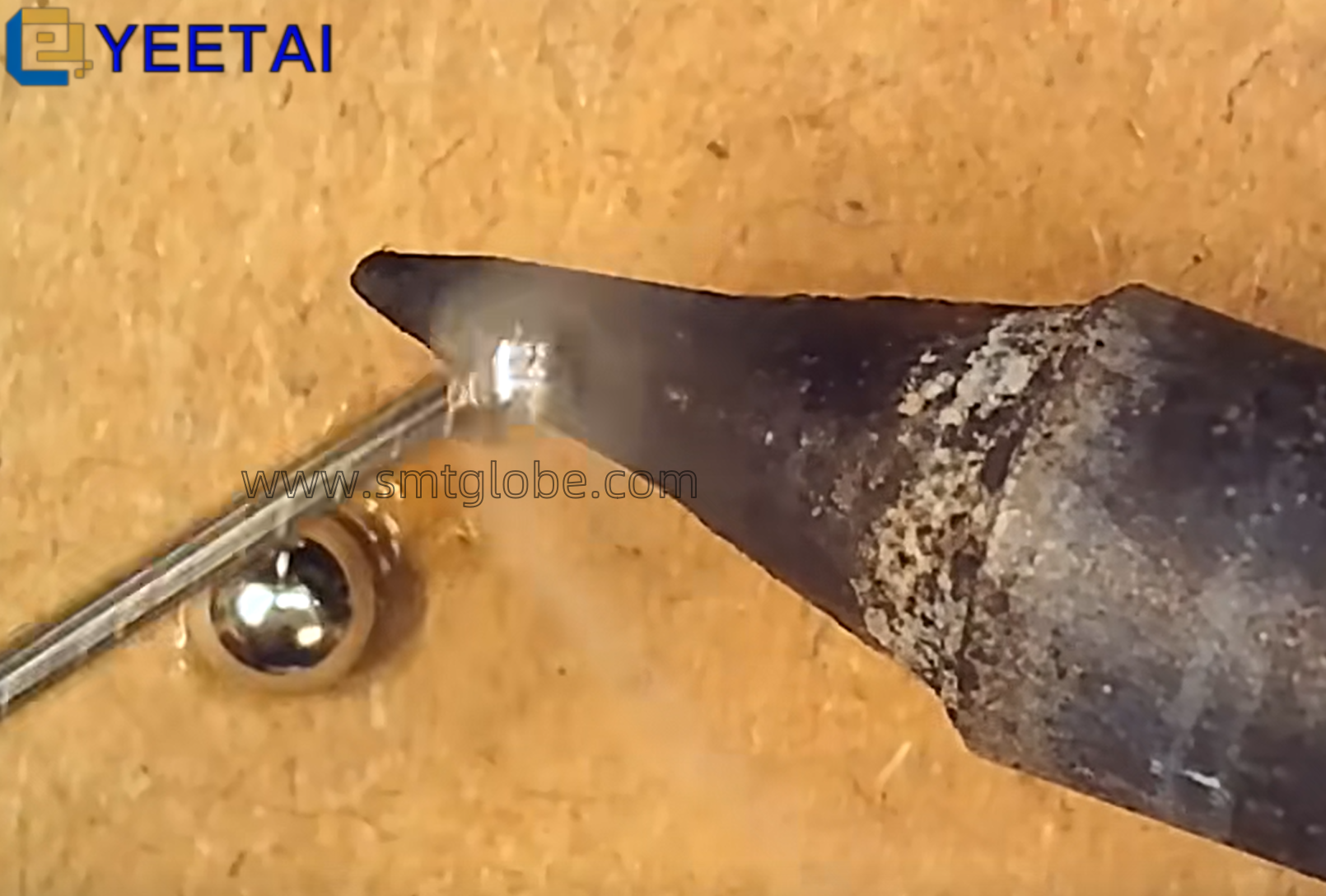
3. Improper Pickup Position
Cause Analysis: If the nozzle does not pick components from the center of the surface, it can lead to significant errors in the image recognition system and result in discards. Incorrect settings for pickup height can also contribute to this issue.
Solution: Adjust the coordinates for component pickup and reset the pickup height, typically setting it to -0.5 mm for tape materials.
4. Faulty Vision Recognition System
Cause Analysis: A dirty recognition lens can impede proper component identification. Suboptimal brightness adjustment settings may result in inadequate contrast for the components.
Solution: Use a lint-free cloth and alcohol to clean the recognition lens, and adjust or replace the components’ encapsulation to obtain better contrast.
5. Feeder Issues
Cause Analysis: Feeders that are magnetic or deformed can affect the smoothness of material delivery.
Solution: Replace faulty feeders promptly and mark them for maintenance or replacement to avoid future issues.
6. Incorrect Program Parameters
Cause Analysis: Improper settings in the programming of component parameters can lead to recognition errors, resulting in discards.
Solution: Modify the component parameters to establish optimal values for accurate recognition.
7. Insufficient Air Pressure
Cause Analysis: Low air pressure can prevent components from being picked up or lead to them falling off during the movement of the pick-and-place head.
Solution: Adjust the equipment air pressure to a range of 0.42-0.45 MPa.
8. Issues with Supplied Materials
Cause Analysis: Components received from customers or purchased by the company may have deformed or oxidized leads, affecting effective placement.
Solution: Conduct rigorous IQC (Incoming Quality Control) checks on materials before processing and work with suppliers to ensure replacement of defective components.
Conclusion
Addressing the issue of component discards in SMT assembly is vital for improving production efficiency. By identifying the causes and implementing solutions, manufacturers can minimize waste, enhance the accuracy of component placement, and ultimately achieve better productivity.
At YEETAI, we produce all kinds of feeder to upgrade SMT machines.