Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are revolutionizing the logistics and manufacturing sectors by providing efficient and automated material transportation. These vehicles can autonomously transport goods from their starting point to their destination while avoiding obstacles along the way. With high flexibility, automation, and intelligence, AGVs can adapt their travel paths based on warehouse layout requirements and production processes. Here, we tell 4 functions of AGVs that make them indispensable in modern automated systems.
1. Route Planning
One of the standout features of AGVs is their ability to operate 24/7. These vehicles can automatically plan their routes in real-time, significantly enhancing the efficiency of cargo handling. Key tasks include supplying materials, picking up goods, weighing items, charging batteries, and independent navigation. This intelligent route planning enables AGVs to optimize their operations, ensuring timely deliveries and reducing downtime.
2. System Adaptability
AGVs can seamlessly integrate with various software systems such as Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), and more. This adaptability allows AGVs to provide real-time insights into vehicle operation, historical performance data, and operational logs. Such integration enhances overall operational efficiency and ensures that AGVs can function effectively within diverse environments.
3. Fault Detection
AGVs are equipped with robust fault detection capabilities, crucial for maintaining operational integrity. In case of any operational anomalies, users can access the vehicle monitoring system to analyze the AGV’s status and review operational logs. This data-driven approach allows for timely troubleshooting and minimizes disruptions in the workflow, ensuring that any issues are swiftly addressed.
4. Intelligent Operation
The intelligent management systems of AGVs can record and process order information, implement order fulfillment, and transmit relevant parameters for monitoring. Daily tasks, such as inventory management and order tracking, can be efficiently handled through the AGV’s vehicle monitoring system. This level of automation not only streamlines operations but also reduces the potential for human error, contributing to higher productivity.
Conclusion
The functionalities of AGVs—route planning, system adaptability, fault detection, and intelligent operation—make them essential components in today’s automated warehouse and manufacturing environments. By enhancing efficiency, flexibility, and reliability, AGVs are paving the way for the future of logistics and production. As industries continue to embrace automation, the role of AGVs will only become more prominent, solidifying their status as critical assets in modern supply chain management.
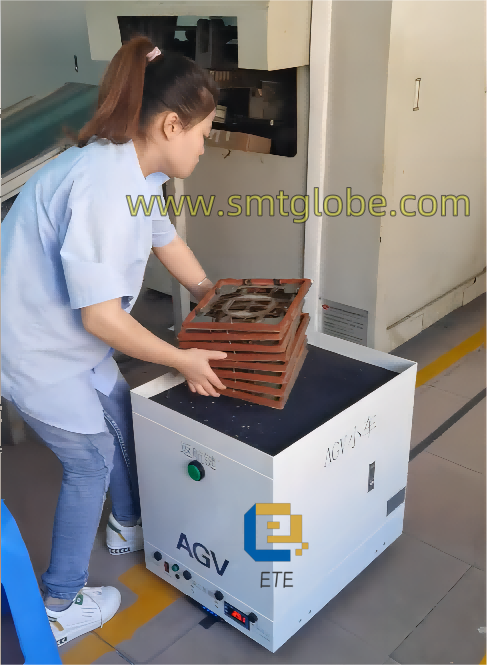
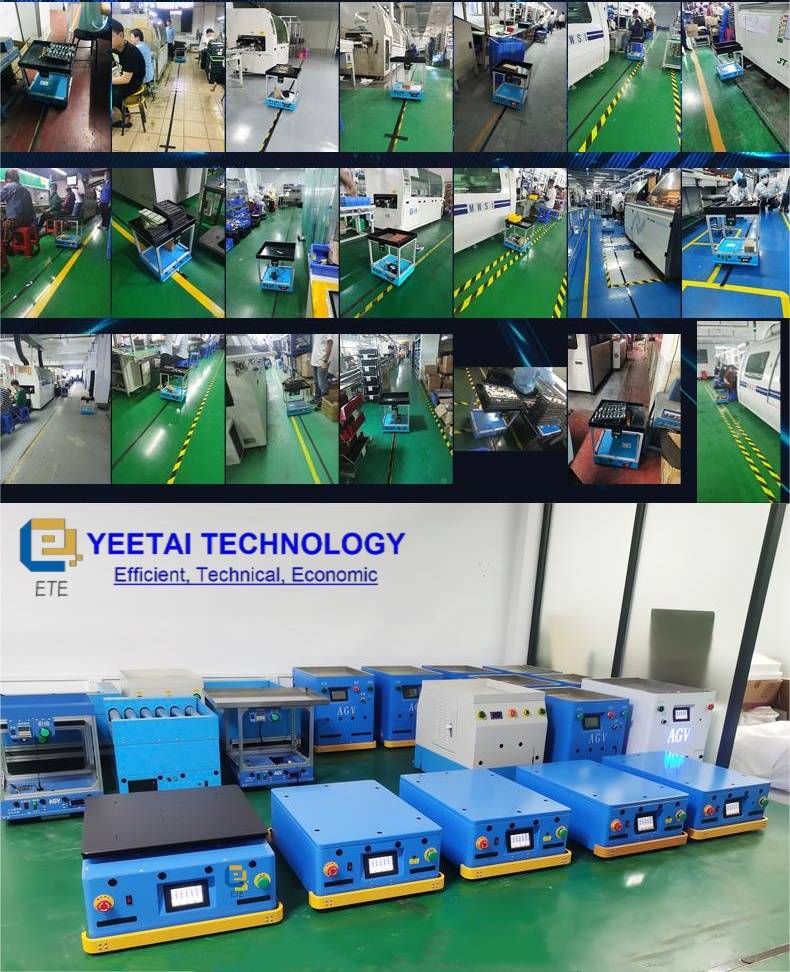


If you need any solutions, we are here to help.
Laser-guided SMT AGV Robot ETE-AGV-910A
SMT AGV Equipment for moving wave soldering pallet | ETE-AGV30-C
SMT Automatic Guided Vehicle ETE-AGV100-T
AGV for PCB moving | ETE-AGV100-L
Wave Soldering Pallet AGV | ETE-AGV60