Ensuring proper management and usage of anti-static devices (ESD consumables) and tools is crucial in minimizing static risks and protecting sensitive electronic components. Here are 10 essential guidelines for effective anti-static management in your workshop:
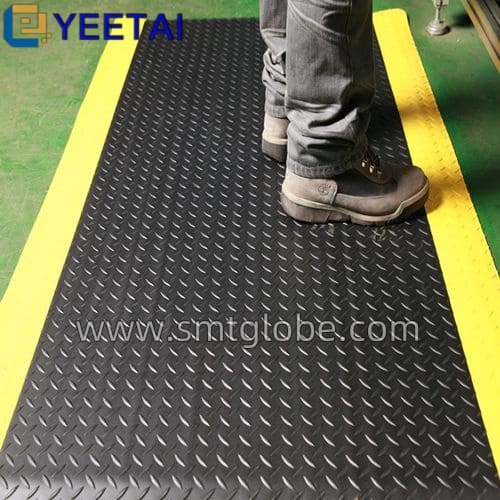
1. Install Anti-Static Flooring
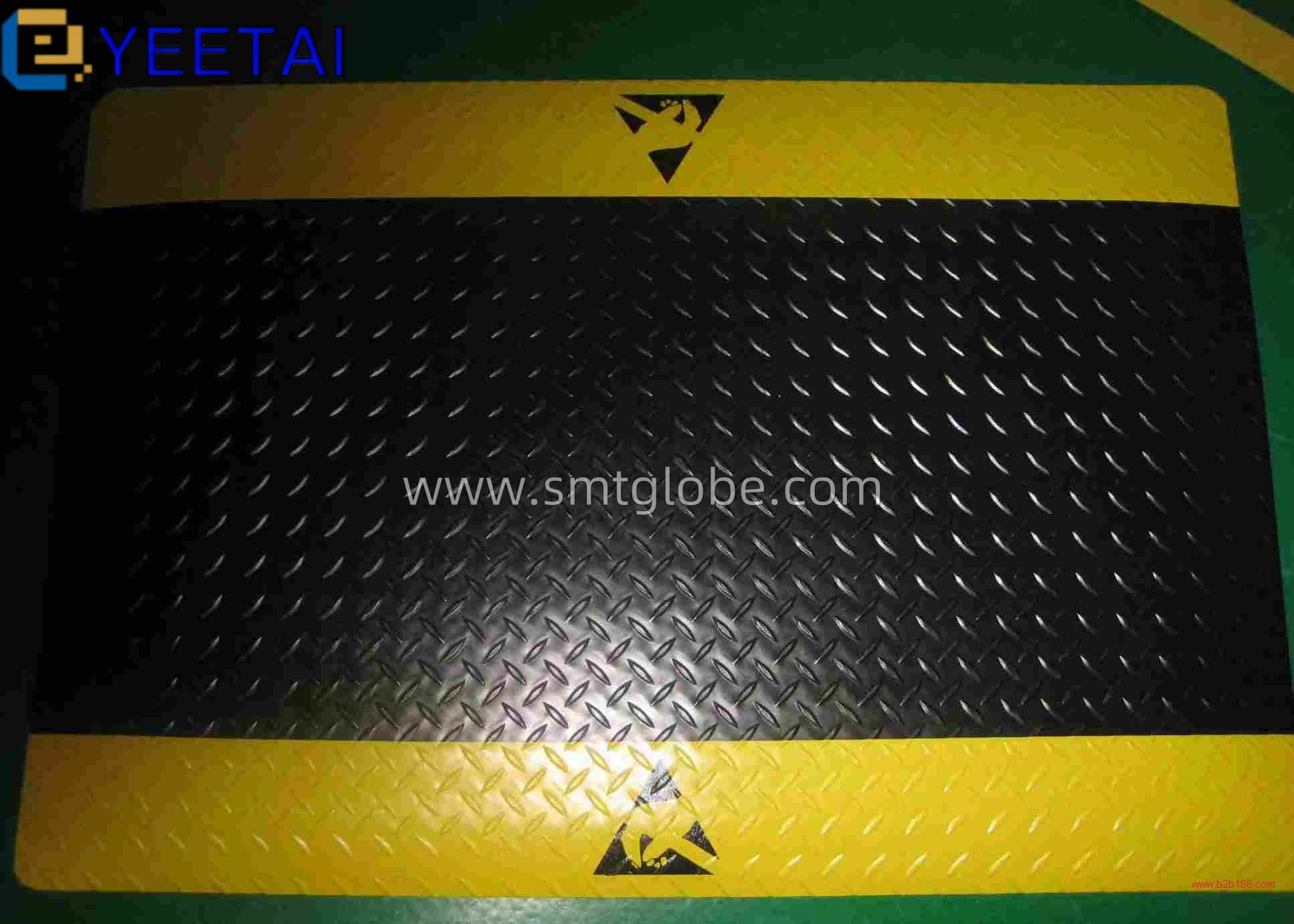
Properly install anti-static flooring in your work area to prevent electrostatic discharge. Avoid placing heavy equipment directly on the floor to prevent deformation. If you must place large equipment, use a 2mm thick steel plate beneath it to distribute weight evenly.
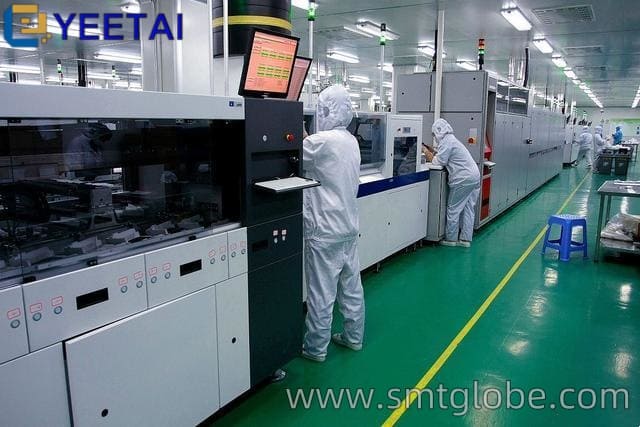



2. Set Up Static Safety Workbenches
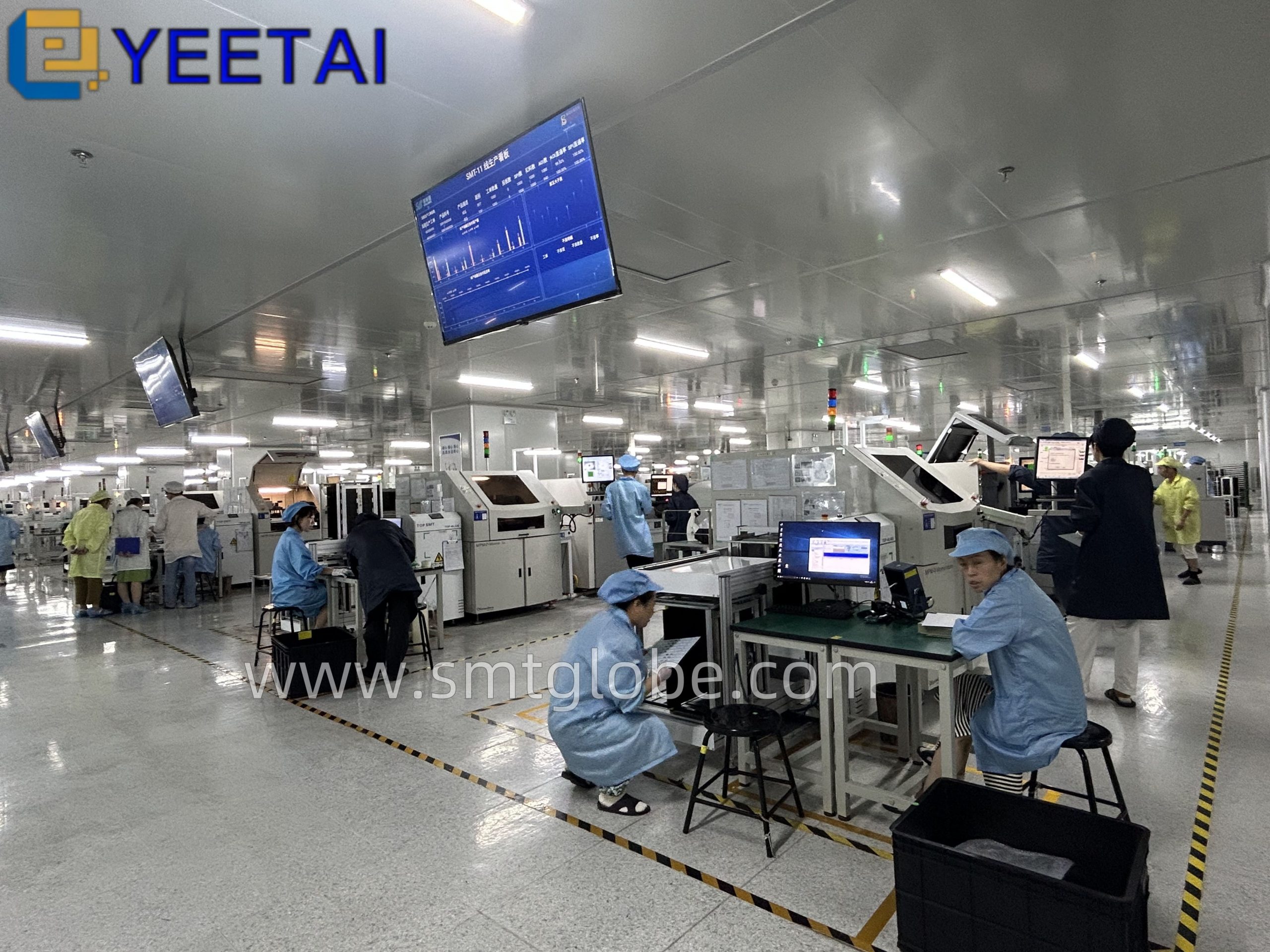

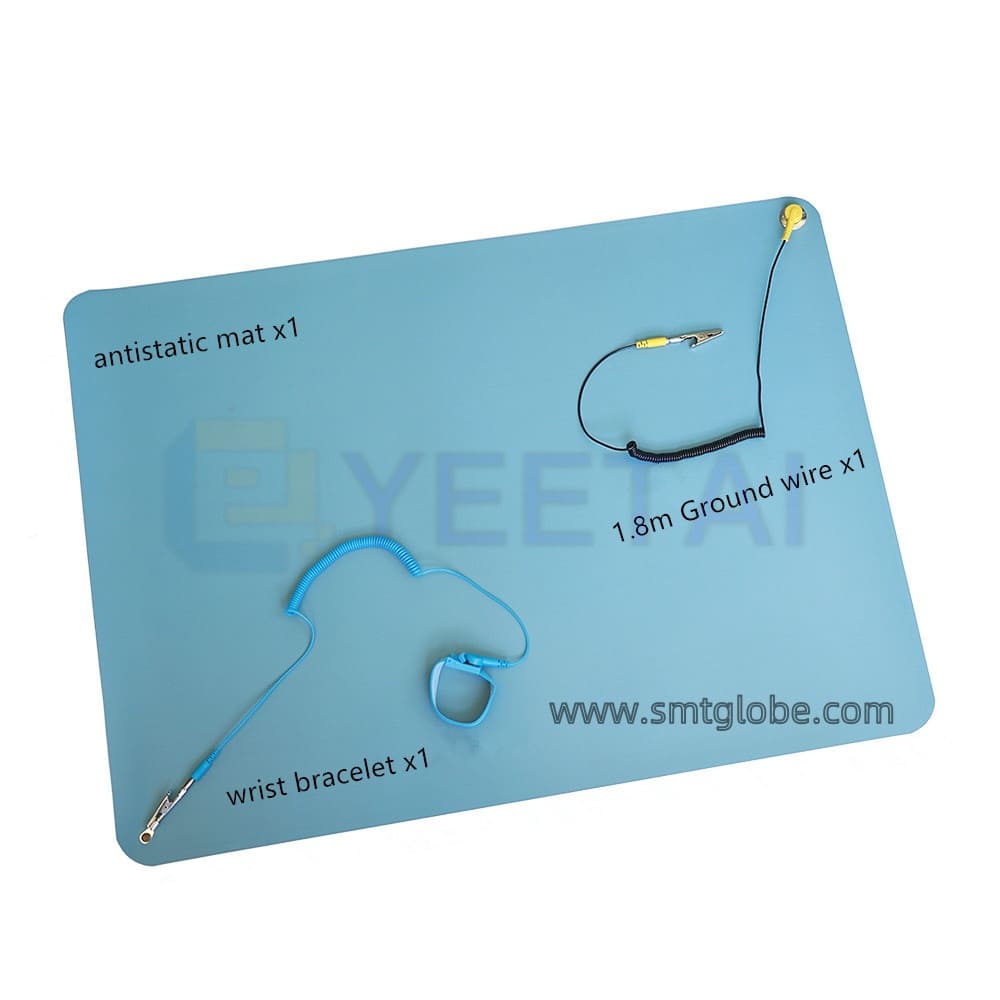
Equip your work area with static safety workbenches, which include:
- Anti-static mats
- Wrist strap connectors
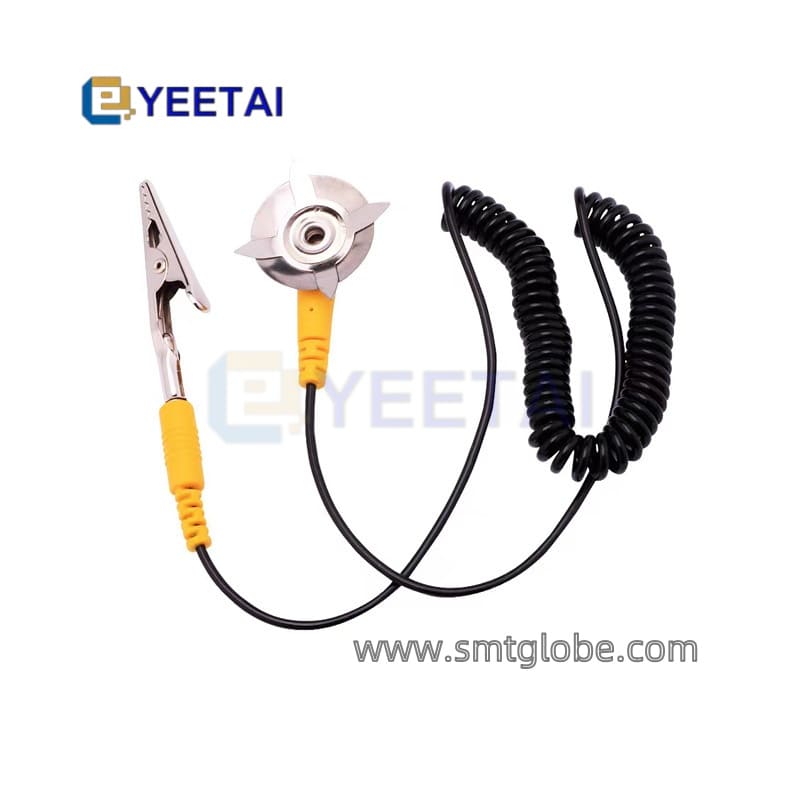
- Grounding wires
Ensure there are at least two wrist strap connectors—one for the operator and another for technicians or inspectors.


3. Keep Workbenches Clear of Static-Prone Items
Refrain from placing items like plastic boxes, rubber, cardboard, and glass on static safety workbenches. Use anti-static document bags for storing important documents to avoid static accumulation.
4. Use Anti-Static Wrist Straps
Personnel handling static-sensitive components must wear anti-static wrist straps. Ensure good skin contact, and verify that the wrist strap system has a resistance to ground of 1MΩ.

5. Utilize Anti-Static Containers
All component storage should utilize ESD-compatible containers, such as:
- ESD bags
- ESD PCB storage trolleys
- ESD magazine racks
Avoid using metal and ordinary containers, and ensure all containers are properly grounded.
6. Wear Anti-Static Work Clothing
Staff entering static-sensitive areas or handling SMD components should wear anti-static work clothing. In dry environments, especially when humidity is below 50%, ensure the clothing meets national standards.
7. Ensure Proper Footwear
Individuals must wear anti-static shoes when entering the work area. For those in regular shoes, use conductive shoe straps or anti-static shoe covers to mitigate static risks.
8. Implement Anti-Static Measures on Conveyors
Install anti-static grounding brushes and supports on production line conveyors and drive shafts. Consider using an ESD ionizer to eliminate static electricity on conveyor surfaces.
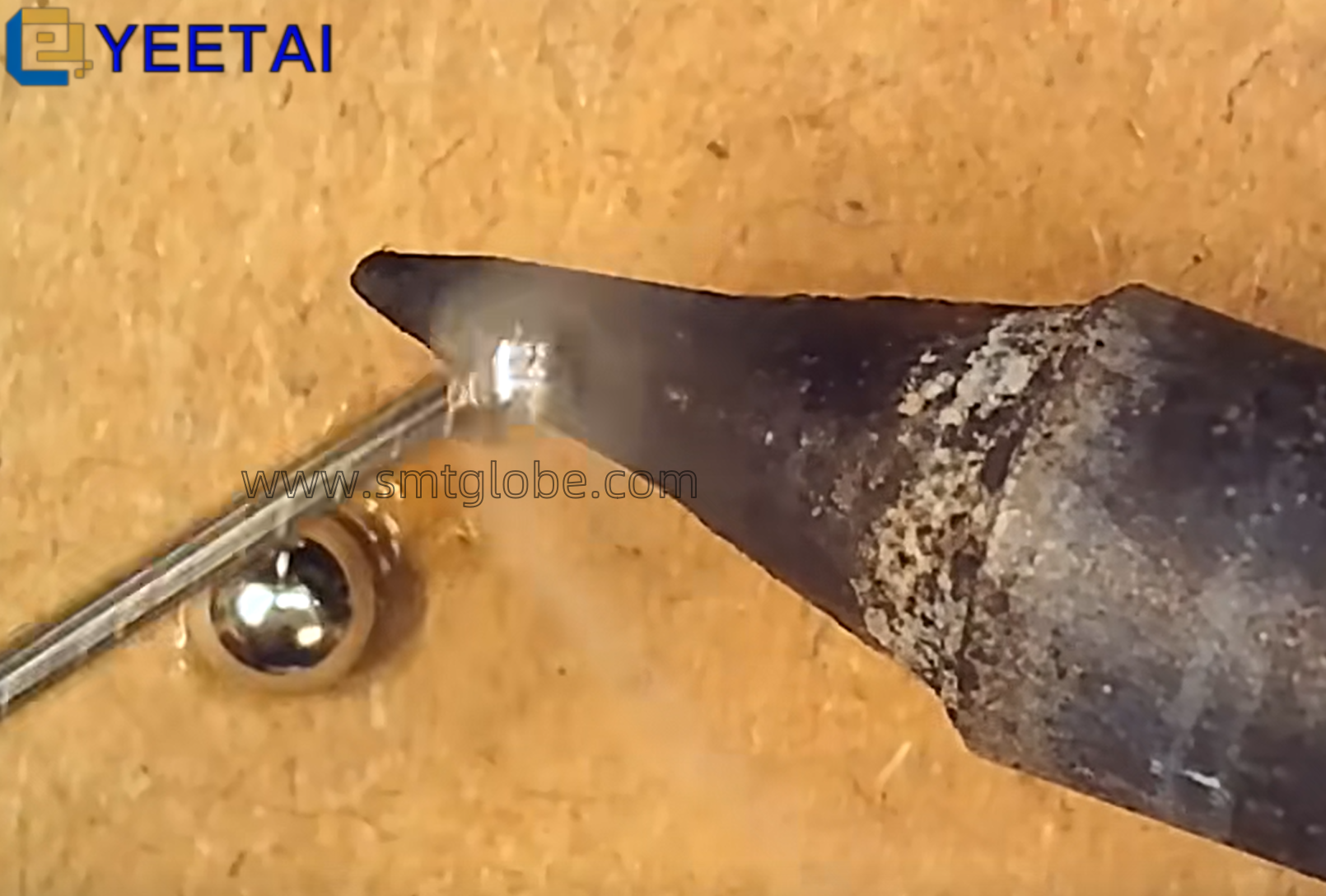
9. Ground All Tools and Equipment
Ensure that assembly fixtures, inspection tools, soldering tools, and various instruments are equipped with proper grounding to prevent static accumulation.
10. Conduct Anti-Static Testing at Entry Points
Install an anti-static testing station at the entrance of your production area. Require all personnel to undergo testing before entry, ensuring they meet safety standards.
Conclusion
Following these 10 essential guidelines for managing and using anti-static equipment will significantly reduce static-related risks and protect sensitive electronic components in your workshop. Regular training and awareness of static control practices are vital to maintaining a safe working environment.